[数据结构 - 第3章] 线性表之单链表(C++实现)
2024-08-31 15:34:01
一、类定义
单链表类的定义如下:
#ifndef SIGNALLIST_H
#define SIGNALLIST_H
typedef int ElemType; /* "ElemType类型根据实际情况而定, 这里假设为int */
/* 线性表的单链表存储结构 */
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data; // 数据域
struct node *next; // 指针域
}Node, LinkList;
class SignalList
{
public:
SignalList(int size = 0); // 构造函数
~SignalList(); // 析构函数
void clearList(); // 清空顺序表操作
bool isEmpty(); // 判断是否为空操作
int getLength(); // 获取顺序表长度操作
bool insertList(int i, const ElemType e); // 插入元素操作
bool deleteList(int i, ElemType *e); // 删除元素操作
bool getElem(int i, ElemType *e); // 获取元素操作
bool insertListHead(const ElemType e); // 头部后插入元素操作
bool insertListTail(const ElemType e); // 尾部后插入元素操作
void traverseList(); // 遍历顺序表
int locateElem(const ElemType e); // 查找元素位置操作
private:
LinkList *m_pList; // 单链表指针
};
#endif
二、构造函数
为头结点m_pList申请内存,数据域置为 0,指针域指向空。
// 构造函数
SignalList::SignalList(int size)
{
// 初始化单链表
m_pList = new Node;
m_pList->data = 0;
m_pList->next = NULL;
}
三、析构函数
调用清空单链表方法,并且销毁头结点。
// 析构函数
SignalList::~SignalList()
{
clearList(); // 清空单链表
delete m_pList;
m_pList = NULL;
}
四、清空链表操作
循环销毁除头结点外的各结点。
// 清空链表操作
void SignalList::clearList()
{
Node *cur; // 当前结点
Node *temp; // 事先保存下一结点,防止释放当前结点后导致“掉链”
cur = m_pList->next; //指向第一个结点
while (cur)
{
temp = cur->next; // 事先保存下一结点,防止释放当前结点后导致“掉链”
delete cur; // 释放当前结点
cur = temp; // 将下一结点赋给当前结点
}
cur->next = NULL; // 注意还要将头结点的指针域指向空
}
清空链表和析构函数的区别:清空链表是循环销毁除头结点外的各结点,析构函数是销毁所有结点,包括头结点。
五、判空和获取顺序表长度操作
// 判断是否为空操作
bool SignalList::isEmpty()
{
return m_pList->next == NULL ? true : false;
}
// 获取链表长度操作
int SignalList::getLength()
{
Node *cur = m_pList;
int length = 0;
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
length++;
}
return length;
}
六、插入元素操作
注意这里是有头结点,头结点作为位置 0,所以只能在位置 1 以及后面插入,所以 i 至少为1。
// 插入元素操作
bool SignalList::insertList(int i, const ElemType e)
{
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!m_pList)
{
cout << "list not exist!" << endl;
return false;
}
// 只能在位置1以及后面插入,所以i至少为1
if (i < 1)
{
cout << "i is invalid!" << endl;
return false;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
Node *front = m_pList; // 这里是让front与i不同步,始终指向j对应的前一个结点
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为1,对应front指向的下一个结点,即插入位置结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front == NULL)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return false;
}
}
// 创建一个空节点,存放要插入的新元素
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = e;
temp->next = NULL;
// 插入结点s
temp->next = front->next;
front->next = temp;
return true;
}
七、删除元素操作
注意提前保存要删除的结点,避免删除结点后丢失。
// 删除元素操作
bool SignalList::deleteList(int i, ElemType *e)
{
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!m_pList)
{
cout << "list not exist!" << endl;
return false;
}
// 只能删除位置1以及后面的结点
if (i < 1)
{
cout << "i is invalid!" << endl;
return false;
}
// 找到i位置所在的前一个结点
Node *front = m_pList; // 这里是让front与i不同步,始终指向j对应的前一个结点
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) // j为计数器,赋值为1,对应front指向的下一个结点,即插入位置结点
{
front = front->next;
if (front->next == NULL)
{
printf("dont find front!\n");
return false;
}
}
// 提前保存要删除的结点
Node *temp = front->next;
*e = temp->data; // 将要删除结点的数据赋给e
// 删除结点
front->next = front->next->next;
// 销毁结点
delete temp;
temp = NULL;
return true;
}
八、遍历操作
遍历前需要判断链表是否存在。
// 遍历链表
void SignalList::traverseList()
{
// 判断链表是否存在
if (!m_pList)
{
cout << "list not exist!" << endl;
return;
}
Node *cur = m_pList->next;
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->data << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
}
九、主函数执行
在主函数中执行的代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "signalList.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 初始化链表
SignalList signleList(20);
cout << "插入元素0-2到链表!" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i<3; i++)
{
signleList.insertList(i+1, i);
}
cout << endl;
// 在位置2插入元素9到链表
cout << "在位置2插入元素9到链表!" << endl << endl;
signleList.insertList(2, 9);
// 在位置3删除元素
int value1;
if (signleList.deleteList(3, &value1) == false)
{
cout << "delete error!" << endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
cout << "在位置3删除元素,删除的元素为:" << value1 << endl << endl;
}
// 查找元素位置
int index = signleList.locateElem(9);
if (index == -1)
{
cout << "locate error!" << endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
cout << "查找到元素9的位置为:" << index << endl << endl;
}
// 遍历链表
cout << "遍历链表: ";
signleList.traverseList();
cout << endl << endl;
// 清空链表
cout << "清空链表!" << endl << endl;
signleList.clearList();
return 0;
}
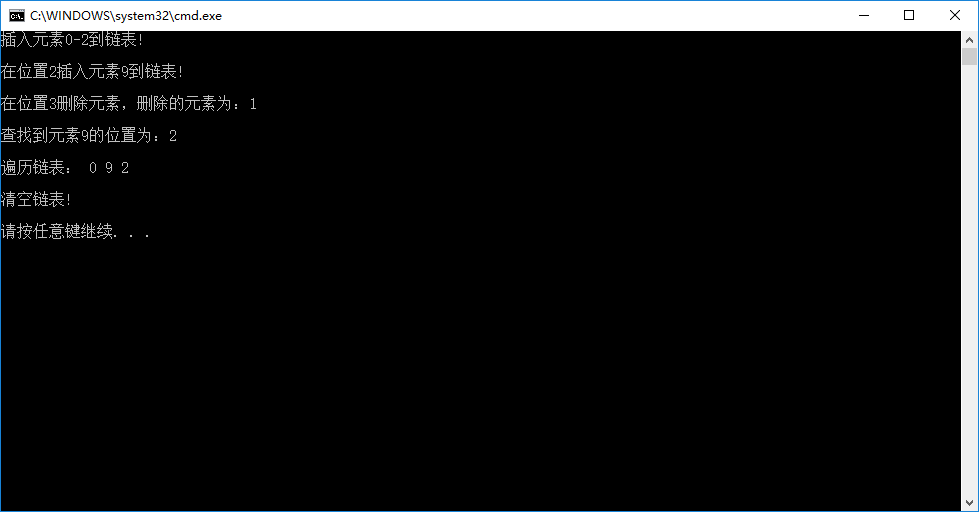
输出结果如下图所示(编译器为VS2013):
最新文章
- Monte Carlo方法简介(转载)
- 拓扑排序 --- hdu 4948 : Kingdom
- AngularJS快速入门指南08:表格
- PHP中使用数组指针函数操作数组示例
- CSRF简单介绍及利用方法-跨站请求伪造
- call stack 如何调用
- Python笔记2-20151023
- eclipse清除运行Maven build...后积累的配置项
- 【转】Linux下软、硬链接的创建和删除
- 01 Android修改新建虚拟机存放的位置
- Android Studio升级3.2.1后的合并XML出错的解决方案
- 简单快捷使用Git
- python中的过滤fliter
- select 数字/字符串/count(参数)/sum(数字) from table
- centos7.5下安装teamview
- Ubuntu防火墙配置
- Linux 文件授权
- 用jquery将输入的文字的双向绑定
- Nginx做转发
- scanf printf gets() puts(),cin cout