TensorFlow实战第四课(tensorboard数据可视化)
tensorboard可视化工具
tensorboard是tensorflow的可视化工具,通过这个工具我们可以很清楚的看到整个神经网络的结构及框架。
通过之前展示的代码,我们进行修改从而展示其神经网络结构。
一、搭建图纸
首先对input进行修改,将xs,ys进行新的名称指定x_in y_in
这里指定的名称,之后会在可视化图层中inputs中显示出来
xs= tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1],name='x_in')
ys= tf.placeholder(tf.loat32, [None, 1],name='y_in')
使用with.tf.name_scope('inputs')可以将xs ys包含进来,形成一个大的图层,图层的名字就是
with.tf.name_scope()方法中的参数
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
# define placeholder for inputs to network
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
接下来编辑layer
编辑前的代码片段:
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, )
return outputs
编辑后
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
Weights= tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
# and so on...
定义完大的框架layer后,通知需要定义里面小的部件weights biases activationfunction
定义方法有两种,一是用tf.name_scope(),二是在Weights中指定名称W
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#define layer name
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
#define weights name
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights= tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]),name='W')
#and so on......
接着定义biases,方法同上
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#define layer name
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
#define weights name
with tf.name_scope('weights')
Weights= tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]),name='W')
# define biase
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
# and so on....
最后编辑loss 将with.tf.name_scope( )添加在loss上方 并起名为loss
这句话就是绘制了loss
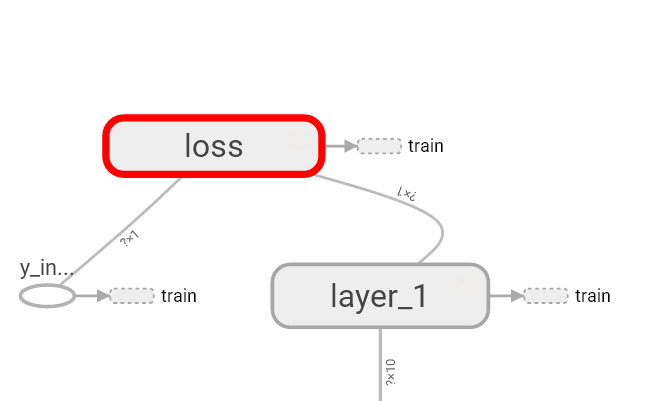
最后再对train_step进行编辑
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
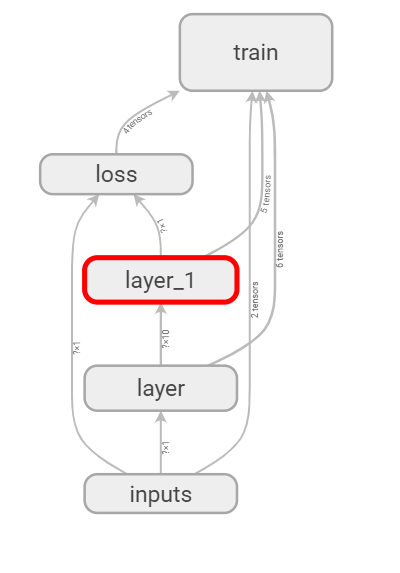
我们还需要运用tf.summary.FileWriter( )将上面绘画的图保存到一个目录中,方便用浏览器浏览。
这个方法中的第二个参数需要使用sess.graph。因此我们把这句话放在获取session后面。
这里的graph是将前面定义的框架信息收集起来,然后放在logs/目录下面。
sess = tf.Session() # get session
# tf.train.SummaryWriter soon be deprecated, use following
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", sess.graph)
最后在终端中使用命令获取网址即可查看
tensorboard --logdir logs
完整代码:
#如何可视化神经网络 #tensorboard import tensorflow as tf def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]), name='W')
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1, name='b')
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs # define placeholder for inputs to network
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='x_input')
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='y_input') # add hidden layer
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None) # the error between prediciton and real data
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) sess = tf.Session() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", sess.graph) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
tensorflow可视化训练过程的图标是如何制作的?
首先要添加一些模拟数据。nump可以帮助我们添加一些模拟数据。
利用np.linespace()产生随机的数字 同时为了模拟更加真实 我们会添加一些噪声 这些噪声是通过np.random.normal()随机产生的。
x_data= np.linspace(-1, 1, 300, dtype=np.float32)[:,np.newaxis]
noise= np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape).astype(np.float32)
y_data= np.square(x_data) -0.5+ noise
在layer中为weights biases设置变化图表
首先我们在add_layer()方法中添加一个参数n_layer 来标识层数 并且用变量layer_name代表其每层的名称
def add_layer(
inputs ,
in_size,
out_size,
n_layer,
activation_function=None):
## add one more layer and return the output of this layer
layer_name='layer%s'%n_layer ## 定义一个新的变量
## and so on ……
接下来 我们层中的Weights设置变化图 tensorflow中提供了tf.histogram_summary( )方法,用来绘制图片,第一个参数是图表的名称,第二个参数是图标要记录的变量。
def add_layer(inputs ,
in_size,
out_size,n_layer,
activation_function=None):
## add one more layer and return the output of this layer
layer_name='layer%s'%n_layer
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights= tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]),name='W')
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/weights', Weights)
##and so no ……
同样的方法我们对biases进行绘制图标:
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1, name='b')
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases)
至于activation_function( ) 可以不用绘制,我们对output 使用同样的方法
最后通过修改 addlayer()方法如下所示
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, n_layer, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer #对神经层进行命名
layer_name = 'layer%s' % n_layer
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]), name='W')
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/weights', Weights)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1, name='b')
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, )
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/outputs', outputs)
return outputs
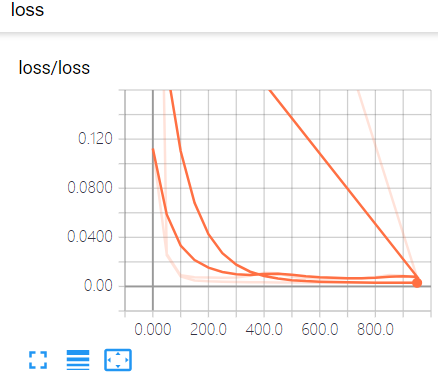
设置loss的变化图
loss是tensorb的event下面的 这是由于我们使用的是tf.scalar_summary()方法。
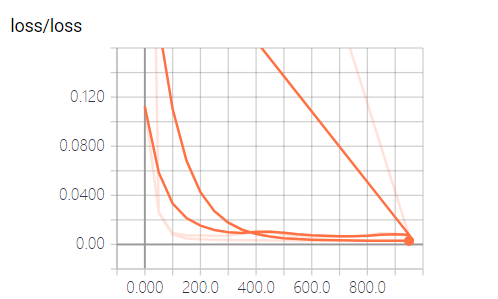
当你的loss函数图像呈现的是下降的趋势 说明学习是有效的
将所有训练图合并
接下来进行合并打包,tf.merge_all_summaries()方法会对我们所有的summaries合并到一起
sess = tf.Session()
#合并
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", sess.graph) init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
训练数据
忽略不想写
完整代码如下:(运行代码后需要在终端中执行tensorboard --logdir logs)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, n_layer, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer #对神经层进行命名
layer_name = 'layer%s' % n_layer
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]), name='W')
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/weights', Weights)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1, name='b')
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, )
tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/outputs', outputs)
return outputs # Make up some real data
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise # define placeholder for inputs to network
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='x_input')
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name='y_input') # add hidden layer
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, n_layer=1, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, n_layer=2, activation_function=None) # the error between prediciton and real data
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),
reduction_indices=[1]))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) sess = tf.Session()
#合并
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", sess.graph) init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init) for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
result = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
#i 就是记录的步数
writer.add_summary(result, i)
tensorboard查看效果 使用命令tensorboard --logdir logs
最新文章
- java在cmd下编译和执行引用jar的类
- 十个最适合 Web 和 APP 开发的 NodeJS 框架
- Supplemental Logging
- replace和replaceAll(路径反斜杠问题)
- 【POJ】【1637】Sightseeing tour
- richTextBox设置选中的字体属性
- 淘特房产CMS系统 7.5
- poj 2356
- Google Guice结合模式
- 1.Date对象
- linux编译内核
- 资源预加载preload和资源预读取prefetch简明学习
- chm制作及Haroopad使用(makedown工具)
- 分布式监控系统Zabbix3.4-钉钉告警配置记录
- WPF之数据触发器 改变控件背景色或闪烁
- Spring Boot 应用系列 5 -- Spring Boot 2 整合logback
- 2018HN多校
- Winform学习之随笔一:Log4net
- golang 生成图表
- 用户登录拦截器查询到登录用户后如何将用户信息传递到后面的Controller