C++类基本--随笔一
2024-10-21 10:02:47
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
Teacher(int m=3,int n=2)
{
a=m;
b=n;
}
void show(); protected:
int a;
int b;
}; void Teacher::show()
{
cout<<a<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Teacher qin;//此处初始化没有参数,可以,是因为有了默认的
qin.show();
return 0;
}
void run(test *p)//利用指针调用
{
cout<<p->rp(100)<<endl;
}
void run(test &p)//利用引用
{
cout<<p.rp(200)<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test a;
run(&a);//指针 用&a
run(a);// 引用,直接a
cin.get();
}
有本书叫 一个月挑战C++,可以下个chm版本来看!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; class ballscore { protected: const static int gbs = 5;//好球单位得分 原先C++ 11前,是不能再类中定义变量初始化的,只能const static ,现在无此限制了 const static int bbs = -3;//坏球单位扣分 float gradescore;//平均成绩 public: float GetGS(float goodball,float badball) //goodball为好球数量,badball为坏求数量
{ int gradescore=0; //新定义一个和成员变量float gradescore相同名字的类成员函数局部变量
ballscore::gradescore = (goodball*gbs + badball*bbs) / (goodball + badball); //由于局部变量与类成员变量同名使用的时候必须在其前加上类名和域区分符
return ballscore::gradescore;//返回平均成绩
}
};
int ballscore=0;//定义一个与类名称相同的普通全局变量
int test;
void main()
{
class test//局部类的创建
{
float a;
float b;
};
test test;
::test=1; //由于局部类名隐藏了外部变量使用需加域区分符
class ballscore jeff; //由于全局变量int ballsocre和类(ballsocre)名称相同,隐藏了类名称,这时候定义类对象需加class前缀以区分
cout<<jeff.GetGS(10,3);
cin.get();
}
- director = new char[10]; strcpy(director,"王大力"); //director = new string; // *director="王大力";//string情况赋值
- class Student { public: Student() { number = 1; score = 100; } void show(); protected: int number; int score; Teacher teacher("王大力");//错误,一个类的成员如果是另外一个类的对象的话,不能在类中使用带参数的构造函数进行初始化 };
类成员的构造是按照在类中定义的顺序进行的,而不是按照构造函数说明后的冒号顺序进行构造的,这一点需要记住! 如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; class Test
{
public:
Test(int j):pb(j),pa(pb+5)
{ }
public:
int pa;
int pb;
};
void main()
{
Test a(10);
cout<<a.pa<<endl;
cout<<a.pb<<endl;
cin.get();
}
pa并没有得到我们所希望的15而是一个随机的任意地址的值。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; class Test
{
public:
Test(int a)
{
kk=a;
cout<<"构造参数a:"<<a<<endl;
}
public:
int kk;
}; void fun_t(int n)
{
static Test a(n);
//static Test a=n;//这么写也是对的
cout<<"函数传入参数n:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"对象a的属性kk的值:"<<a.kk<<endl;
}
Test m(100);
Test n(66);
void main()
{
fun_t(20);
fun_t(30);
cin.get();
}
c++规定,所有的全局对象和全局变量一样都在主函数main()之前被构造,函数体内的静态对象则只构造一次,也就是说只在首次进入这个函数的时候进行构造!,所以上面运行结果:
构造参数a:100
构造参数a:66
构造参数a:20
函数传入参数n:20
对象a的属性kk的值:20
####构造参数a:30###没有这一句,
函数传入参数n:30
对象a的属性kk的值:20
int main()
{
Internet a("中国软件开发实验室","www.cndev-lab.com");
Internet b = a;
cout<<"==========="<<endl;
b.show();
test(b);
} //运行结果如下:, 也就是Internet b=a;时有copy构造,而实际应用时也有!

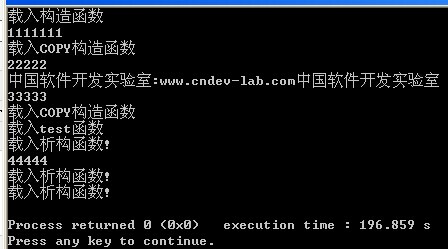
int main()
{
Internet a("中国软件开发实验室","www.cndev-lab.com");
cout<<"1111111\n";
Internet b = a;
cout<<"22222\n";
b.show();
cout<<"33333\n";
test(b);
cout<<"44444\n";
} //运行结果如下:开始没有444的输出,敲回车时才会出现...
最新文章
- 记录rewrite url我之前不知道的地方
- notifyDataSetInvalidated和notifyDataSetChanged有什么区别
- SSMS错误代码大全
- SPOJ4206Fast Maximum Matching(hopcroft-karp)
- CTO的眼界到底有多宽?
- hibernate中的缓存机制
- 一句话输出网站404页面,REFER及相关排序
- php将会话保存在数据库里
- 05_Elasticsearch 单模式下API的增删改查操作
- JavaScript的原型
- Python基础学习参考(六):列表和元组
- JAVA_SE基础——34.static修饰成员变量
- 修复lvm的逻辑卷
- Discuz3.2与Java 项目整合单点登陆
- MACE移植要求
- 传统前端工程使用 Vue 等框架重构的思路
- spring注解之@profile
- Netsharp下载及环境搭建
- C#の----Func,Action,predicate在WPF中的应用
- (笔记)Mysql命令select:当前选择(连接)的数据库