hdu 3873 Invade the Mars(有限制的最短路 spfa+容器)
Invade the Mars
Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 365768/165536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2079 Accepted Submission(s):
612
soon.The evil U.S. decided to invade the Mars to save their lives.
But the
childlike Marsmen never keeps any army,because war never take place on the
Mars.So it's very convenient for the U.S. to act the action.
Luckily,the
Marsmen find out the evil plan before the invadation,so they formed a defense
system.The system provides enchantment for some citys,and the enchantment
generator for city A maybe set in city B,and to make things worse,both city B
and C and more will provide echantment for city A.
The satelite of U.S. has
got the map of the Mars.And they knows that when they enter a city,they can
destory all echantment generator in this city at once,and they can enter a city
only if they has destoryed all enchantment generator for this city,but troops
can stay at the outside of the city and can enter it at the moment its
echantment is destoryed.Of course the U.S. army will face no resistance because
the Mars keep no army,so troops can invade in many way at the same time.
Now
the U.S. will invade the Mars,give you the map,your task is to calculate the
minimium time to enter the capital of the Mars.
number of test cases.
For each testcase:
The first line contains two
integers N and M,1<=N<=3000,1<=M<=70000,the cities is numbered from
1 to N and the U.S. landed on city 1 while the capital of the Mars is city
N.
The next M lines describes M paths on the Mars.Each line contains three
integers ai,bi and wi,indicates there is a unidirectional path form ai to bi
lasts wi minutes(1<=wi<=10^8).
The next N lines describes N citys,the
1+M+i line starts with a integer li,followed with li integers, which is the
number of cities has a echantment generator protects city i.
It's guaranteed
that the city N will be always reachable.
minimium time needed to enter the capital of the Mars.
The Map is like this: We can follow these ways to achieve the fastest speed: 1->2->3,1->2->5,1->4->6。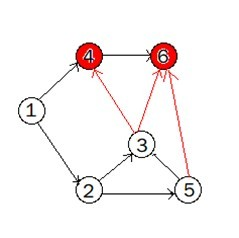
进攻n个城市,有些城市可能受其他城市保护,
如果i城市受j城市保护,那么你必须先攻占j城市才能再攻占i城市,问你攻占城市n的最短时间是多少。
数据解释:
给定t, 表示有t组数据
给定n,m 表示n个点,m条边
接下来m条有向边, a,b,c 表示从a到b,距离为c
接下来n行, 每行第一个整数d,然后接下来是d个整数,x1,x2,...xd, 表示第i个城市受d个城市保护,表示只有城市x1,x2...xd都被攻占,城市i才能被攻占
问从点1到达点n的最短时间(一定是可达的)
重要的一点是,因为是军队,所以可以同时进军多个点。
参照网上大神的思路:
用一个数组pt记录某城市被保护的次数(城墙的耐久度)。当pt[i]==0时,并且该城市没有被占领,那么军队占领该城市的时间dist[i]=max(dist[i], dn[i]),其中dn[i]表示该城市脱离保护的时间(也就是该城市可能被占领的最小时间)。此时,如果j城市(未被占领)与i城市相邻,则dist[j]=dist[i] + w, w是e[i][j]的边权。这样就有一个大致的模型了。还要注意,在确定i城市被占领的时间的时候,要判断军队是否能到达i城市。也就是判断dist[i]!=INF?
为了避免dist[]不断松弛,需要用优先队列。每次弹出来的点能保证是到达该点的最短距离。当某点不收保护时,就入队。最短距离如果已经确定,就标记,不用再去更新距离(其实无法更新,因为已经是最短距离)。
在知道i点的最短距离后,去计算相邻的j点的最短距离时。需要dist[i]和i。因为是按照最短距离的大小而弹出队列的,dist[i]需要入队。占领i城市以后,它所保护的城市将不再收到它的保护。需要枚举。所以需要将i入队。然后就用了pair函数。
附上代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define M 70005
#define N 3005 typedef pair <long long, int > pii; struct Edge
{
int from,to,val;
int next;
} edge[M]; int n,m,tol;
int head[M],pt[N];
long long dis[N],dn[N]; ///dis记录行走的距离时间,dn记录解除保护的时间
bool vis[N];
vector<int> p[N]; ///容器 int max(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
} void addEdge(int u,int v,int val)
{
edge[tol].from=u;
edge[tol].to=v;
edge[tol].val=val;
edge[tol].next=head[u];
head[u]=tol++;
} void spfa(int s)
{
memset(dis,INF,sizeof(dis));
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii> > q;
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
dis[s]=;
q.push(make_pair(dis[s],s));
while(!q.empty())
{
pii u=q.top();
q.pop();
int x=u.second;
if(vis[x]) continue;
vis[x]=true;
int y=p[x].size();
int k=;
while(k<y) ///被保护的城市
{
int z=p[x][k];
pt[z]--;
dn[z]=max(dn[z],dis[x]);
if(dn[z]!=INF&&pt[z]==)
{
dis[z]=max(dis[z],dn[z]);
q.push(make_pair(dis[z],z));
}
k++;
}
for(int i=head[x]; i!=-; i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].to;
if(dis[v]>dis[x]+edge[i].val)
{
dis[v]=max(dis[x]+edge[i].val,dn[v]);
if(!pt[v]) q.push(make_pair(dis[v],v)); }
}
}
} void init()
{
tol=;
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
memset(dn,,sizeof(dn));
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
p[i].clear();
} int main()
{
int T,i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
init();
int a,b,c;
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
addEdge(a,b,c);
}
for(i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&k);
pt[i]=k;
while(k--)
{
scanf("%d",&j);
p[j].push_back(i);
}
}
spfa();
printf("%I64d\n",dis[n]);
}
return ;
}
最新文章
- 2003服务器搭建vpn
- linux 下vim的使用
- Oracle 权限查询
- JS手机定位地理位置
- 2064: 分裂 - BZOJ
- 点击按钮弹出div,留用
- Ext.net中常用的三种交互方式
- 已知整数m,n,p,q适合(m-p)|(mn+pq)证明:(m-p)|(mq+np)(整除理论1.1.5)
- 15.找出如下数组中最大的元素和最小的元素, a[][]={{3,2,6},{6,8,2,10},{5},{12,3,23}}
- C语言 - pthread
- weex里Vuex state使用storage持久化
- 导出MySql中的数据库 --Linux/Windows
- loj 10050 连续子段最大异或和
- 【转】HashMap实现原理及源码分析
- 决策树(ID3,C4.5,CART)原理以及实现
- Linux 命令详解(七)Systemd 入门教程:命令篇
- tornado请求头/状态码/接口 笔记
- 014 再次整理关于hadoop中yarn的原理及运行
- Rokid开发者社区skill之【历史上的今天】
- [arc068E]Snuke Line-[树状数组]