【C#进阶学习】泛型
2024-10-20 08:46:05
一、泛型引入
需求:传入一个类型(整型/日期/字符串或其他),打印出它的类型和内容。
1.初级版
public class CommonMethod
{
/// <summary>
/// 打印int值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="iParameter"></param>
public static void ShowInt(int iParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, iParameter.GetType().Name, iParameter);
} /// <summary>
/// 打印string值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sParameter"></param>
public static void ShowString(string sParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, sParameter.GetType().Name, sParameter);
} /// <summary>
/// 打印DateTime值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="dParameter"></param>
public static void ShowDateTime(DateTime dParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, dParameter.GetType().Name, dParameter);
}
}
typeof和gettype的区别
调用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
int i = ;
string test = "test";
object o = new object();
CommonMethod.ShowDateTime(dt);
CommonMethod.ShowInt(i);
CommonMethod.ShowString(test);
}
2.升级版
/// <summary>
/// 打印object值
/// 1.object是一切类型的基础
/// 2.通过集成,子类拥有父类的一切属性和行为
/// </summary>
/// <param name="o"></param>
public static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, oParameter.GetType().Name, oParameter);
}
调用
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
int i = ;
string test = "test";
object o = new object();
CommonMethod.ShowObject(dt);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(i);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(test);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(o);
缺点:如果传递的是值类型,会装箱拆箱
二、泛型来喽
定义泛型
public class GenericMethod
{
/// <summary>
/// 方法名字后面带上尖括号 类型参数
/// T可以换成其他任何未定义的名称,但是不要用关键字、类名等等
/// 来自 .net framework2.0 CLR升级的
/// 解决相同内容/操作,对于不同参数的问题
///
/// 延迟声明,声明方法的时候没有指定参数类型,而是等到调用的时候指定
/// 延迟思想:推迟一切可以推迟的
///
/// 编译的时候 类型参数编译为占位符 `(1旁边英文输入状态)
/// 程序运行的时候,jit即时编译替换为真实类型
///
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="o"></param>
public static void Show<T>(T tParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter);
}
}
调用
GenericMethod.Show<DateTime>(dt);
GenericMethod.Show(dt);//不指定类型参数,编译器自动推算(编译器的语法糖)
GenericMethod.Show<int>(i);
GenericMethod.Show<string>(test);
GenericMethod.Show<object>(o);
三、消耗时间对比
using System;
using System.Diagnostics; namespace MyGeneric
{
public class Monitor
{
public static void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("******************Monitor****************");
int iValue = ;
long commonSecond = ;
long objectSecond = ;
long genericSecond = ; {
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
ShowInt(iValue);
}
watch.Stop();
commonSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
} {
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i=;i<;i++)
{
ShowObject(iValue);
}
watch.Stop();
objectSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
Show(iValue);
}
watch.Stop();
genericSecond = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine("commonSecond={0},objectSecond={1},genericSecond={2}",
commonSecond, objectSecond, genericSecond);
Console.Read();
} public static void ShowInt(int iParameter)
{
//do nothing
} public static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
{
//do nothing
} public static void Show<T>(T tParameter)
{
//do nothing
}
}
}
调试启动的时间如下,可以看出泛型执行的时间是最短的。
如果更换顺序,将执行泛型的方法放到第一位的话,会出现泛型时间和普通时间一样,甚至还会比它耗费时间长的情况。
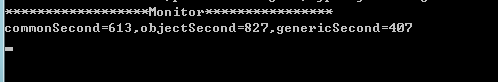
ctrl+F5启动时间对比如下(这一块不懂,为什么普通方法要比泛型的时间快呢)
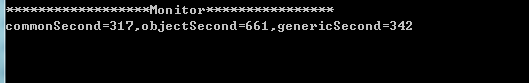
四、泛型类
using System; namespace MyGeneric
{
//泛型类
public class GenericClass<W,Jasmine,Apple>//参数类型可以随便指定,意思就是相当于在这个类中定义了一个w的类型
{
public void Show(W w) { }
public Jasmine Get()
{
return default(Jasmine);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 泛型接口
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
public interface IStudy<T>
{
T Study(T t);
}
public delegate Everything GetHandler<Everything>();//泛型委托 /// <summary>
/// 普通类
/// </summary>
public class Child
//: GenericClass<string,int,string> //指定类型参数后即可继承
//:GenericClass<W, Jasmine, Apple> 这种写法是错误的,普通类不能直接继承泛型类
//:IStudy<T> 普通类不能直接实现泛型接口
: IStudy<string>
{
public string Study(string t)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
} public class GenericChild<W,Jasmine, Apple>
//: GenericClass<W,Jasmine,Apple> //泛型类可以直接继承泛型类
//public class GenericChild<W, Jasmine>//等于声明了两个局部类型 W和Jasmin
//: GenericClass<W, Jasmine, string>
:IStudy<W> //泛型类不能直接实现泛型接口
{
public W Study(W t)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
} }
五、泛型约束
1.所需模型
using System; namespace MyGeneric
{
public class Model
{
public class People
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Hi()
{
}
} public interface ISports
{
void PingPang();
} public interface IWork
{
void Work();
} public class Chinese : People,ISports,IWork
{
public void Tradition()
{
Console.WriteLine("谦虚");
}
public void SayHi()
{
} public void PingPang()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
} public void Work()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
} public class Sichuan : Chinese
{
public string Panda { get; set; }
public void Huoguo()
{
Console.WriteLine("吃火锅啦");
}
}
} }
2.泛型约束(基类约束)
using System;
using static MyGeneric.Model; namespace MyGeneric
{
public class Constraint
{
/// <summary>
/// 有约束才有自由,有权利就得有义务
///
/// 1.基类约束,就可以访问基类的方法和属性(基类/子类)
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <param name="tParameter"></param>
public static void Show<T>(T tParameter) where T : People //基类约束
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={2},type={1}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter); Console.WriteLine(tParameter.Id);
Console.WriteLine(tParameter.Name);
tParameter.Hi();
}
}
}
调用
People people = new People()
{
Id = ,
Name = "张三"
};
Chinese chinese = new Chinese()
{
Id = ,
Name = "李四"
};
Sichuan sichuan = new Sichuan()
{
Id = ,
Name = "小红"
}; Constraint.Show(people);
Constraint.Show(chinese);
Constraint.Show(sichuan);
3.泛型约束(接口约束)
public static void ShowSports<T>(T tParameter) where T : ISports //基类约束
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={2},type={1}",
typeof(CommonMethod).Name, tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter); tParameter.PingPang();
}
调用和上面的相同,实现了该接口的类,可直接当做参数传入。
4.其他泛型约束写法
public static T Get<T>()
//where T:class //引用类型约束
//where T:struct//值类型约束
where T:new() //无参数构造函数约束
{
T t = new T();
return default(T);
}
六、协变
1.相关模型(Sparrow是Bird的子类)
public class Bird
{
} public class Sparrow : Bird
{
}
2.
Bird bird1 = new Bird();
//左边父类,右边子类
Bird bird2 = new Sparrow();
Sparrow sparrow1 = new Sparrow();
List<Bird> birdList1 = new List<Bird>();
//List<Bird> bird3 = new List<Sparrow>(); //不是父子关系,没有继承关系 List<Bird> birdlist2 = new List<Sparrow>().Select(s => (Bird)s).ToList();
3.查看IEnumerable定义,可以看到有一个关键字out
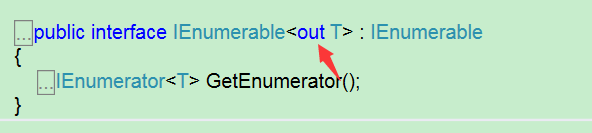
4.下面可实现左边是父类,右边是子类
//协变
IEnumerable<Bird> birdList4 = new List<Bird>();
IEnumerable<Bird> birdList5 = new List<Sparrow>();//协变
5.具体应用
/// <summary>
/// out协变 只能是返回值
/// 协变逆变只存在于接口或者委托
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
public interface ICustomerListOut<out T>
{
T Get();
//void Show(T t); // 此处错误,T不能作为传入参数
} /// <summary>
/// 类没有协变逆变
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
public class CustomerListOut<T> : ICustomerListOut<T>
{
public T Get()
{
return default(T);
}
}
调用
ICustomerListOut<Bird> customerList = new CustomerListOut<Bird>();
ICustomerListOut<Bird> customerList1 = new CustomerListOut<Sparrow>(); //协变
七、逆变
1.定义
public interface ICustomerListIn<in T>
{
//T Get(); void Show(T t);
} /// <summary>
/// 逆变 只能作为参数传入
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
public class CustomerListIn<T> : ICustomerListIn<T>
{
//T Get(); //不能作为返回值 public void Show(T t)
{
}
}
2.调用
//逆变
ICustomerListIn<Sparrow> customerList2 = new CustomerListIn<Sparrow>();
ICustomerListIn<Sparrow> customerList3 = new CustomerListIn<Bird>(); //左边是子类的时候,右边可以是父类 ICustomerListIn<Bird> birdList6 = new CustomerListIn<Bird>();
birdList6.Show(new Sparrow());
birdList6.Show(new Bird());
八、协变逆变混合应用
1.定义
public interface IMyList<in inT, out outT>
{
void Show(inT t);
outT Get();
outT Do(inT t); //out只能是返回值 in只能是参数
} public class MyList<T1, T2> : IMyList<T1, T2>
{ public void Show(T1 t)
{
Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name);
}
public T2 Get()
{
Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name);
return default(T2);
}
public T2 Do(T1 t)
{
Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name);
Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name);
return default(T2);
}
}
2.调用
IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList1 = new MyList<Sparrow, Bird>();
IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList2 = new MyList<Sparrow, Sparrow>(); //协变
IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList3 = new MyList<Bird, Bird>(); //逆变
IMyList<Sparrow, Bird> myList4 = new MyList<Bird, Sparrow>(); //逆变
九、泛型缓存
不太懂,有时间再好好研究下(捂脸......)
最新文章
- 如何用vs2010打开vs2013的项目?
- RabbitMQ、Rdis
- 使用gulp来构建一个前端项目
- jquery 匿名函数的区别
- Peeking Iterator
- Kibana安装及部署
- 【Cocos2d-Js基础教学 入门目录】
- SVN空格问题的解决方法
- spinlock自旋锁de使用
- SRM 581 D2 L3:TreeUnionDiv2,Floyd算法
- TypeScript入门-基本数据类型
- jsp快速开始
- nginx 301重定向一种实现方法
- NN 激活函数 待修改
- header 和http状态码
- Intelij的idea和pycharm的使用
- int和Integer之间的区别和联系
- 删除github上个人的repositories的操作步骤
- ZENCART 菜鸟找人一起学习
- C# Timer定时器用法