if,for,异常,random模块,计算圆周率
2024-09-29 21:25:50
一、分支结构
单分支结构
if 一般用于判断选择
score = 95
if score > 90:
print('优秀')
双分支结构
- if...else
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print('成年')
else:
print('未成年')
- 三目运算
age = 19
print('成年') if age >=18 else print('未成年') # 只有双分支有这种写法
- if...elif...elif...else 与 if...if...if...else
# 90以上优秀,70-90良好,70以下不及格
# 法1:
score = 79
if score > 90:
print('优秀')
elif score > 70:
print('良好')
else:
print('不及格')
# 法2:
score = 79
if score > 90:
print('优秀')
if score > 70 and score < 90:
print('良好')
else:
print('不及格')
if...elif...elif...else 执行完if才到elif 执行if就已经筛选了
if...if...if...if 同时判断 (效率低)
二、异常处理
- 捕获异常
try:
print('----1----')
f = oen('a.txt', 'r') # 路径不对, 是错误的代码
print('----2----')
except: # 捕获异常
pass
# 输出结果:
----1----
- 捕获具体异常
try:
1 / 0
y = input('请输入数字:')
y += 10
except TypeError as e:
print('error:', e)
except ZeroDivisionError as a:
print('error:', a)
print(x + 10)
# 打印结果:
error: division by zero
11
try:
1 / 0
y = input('请输入数字:')
y += 10
except Exception as e: # 只要捕捉Exception
print('error:', e)
不需要记住具体异常,只要捕捉Exception
- finally (无论是否报错,都会执行finally下的代码)
try:
1 / 0
y = input('请输入数字:')
y += 10
except Exception as e: # 只要捕捉Exception
print('error:', e)
finally: # 无论是否报错,都会执行finally下的代码
print(1)
- raise (可以自定义异常)
s = input('请输入数字:')
# print(s.isalpha()) # isalpha() 如果全是字母,则输出True
if s.isalpha():
raise TypeError('报错了, 请输入数字')
# 打印结果:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:/test2.py", line 82, in <module>
raise TypeError('报错了, 请输入数字')
TypeError: 报错了, 请输入数字
三、循环结构
- while循环
count = 0
while count < 10:
if count %2 == 0:
print(count, end=',')
count += 1
# 打印结果:
0,2,4,6,8,
- for循环
for i in range(21):
print(i, end=', ')
# 打印结果:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20,
- 循环 + continue
for i in range(21):
if i == 10:
continue # continue终止本次循环,跳到下次循环
print(i, end=', ')
# 打印结果:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20,
- 循环 + break
for i in range(21):
if i == 10:
break
print(i, end=', ')
# 打印结果:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
四、random模块
- random.randint()
import random
print(random.randint(1,10)) # 随机生成1-10中某个数
print(random.random()) # 在0-1之间默认生成数
- random.random()
import random
random.seed(4) # 给一个随机数种子
print(random.random()) # 只第一次随机生成,之后生成的数字就一样了
print(random.random())
# 如果不自定义种子,则种子按照当前的时间来
- random.choice()
import random
print(random.choice([1,2,3,4,5]))
- random.shuffle()
import random
lt = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
random.shuffle(lt) # 打乱列表顺序
print(lt)
五、计算圆周率
- 公式法计算
圆周率计算公式:
\[\pi = \sum_{k=0}^\infty [\frac{1}{16^k} (\frac{4}{8k+1}-\frac{2}{8k+4}-\frac{1}{8k+5}-\frac{1}{8k+6})]
\]
\]
pi = 0
k = 0
while True:
pi += (1 / (16 ** k)) * (4 / (8 * k + 1) - 2 / (8 * k + 4) - 1 / (8 * k + 5) - 1 / (8 * k + 6))
print(pi)
k += 1
- 蒙特卡罗方法计算圆周率
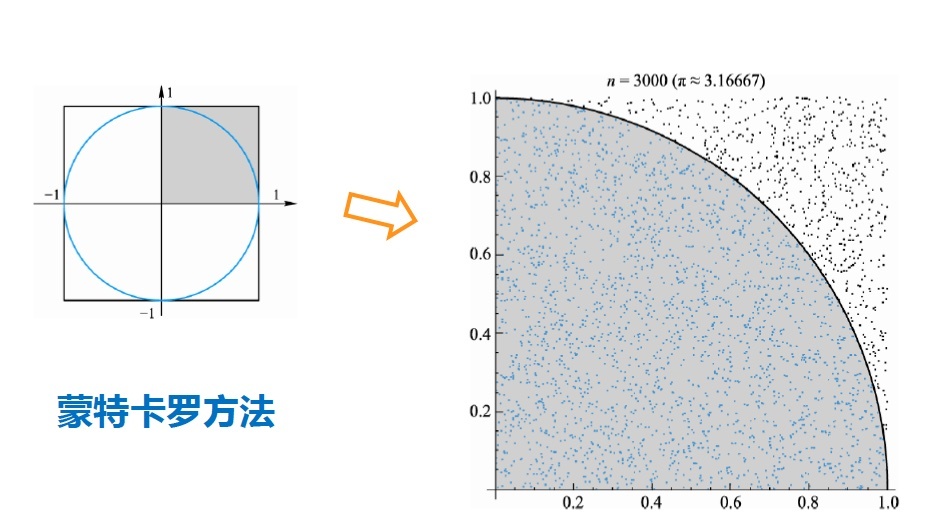
import random
count = 0
for i in range(1000000):
x, y = random.random(), random.random()
distance = pow(x**2 + y**2, 0.5)
if distance < 1:
count += 1
print(count/1000000*4)
最新文章
- Spring远程调用技术<1>-RMI
- PHP curl传 json字符串
- Practical Machine Learning For The Uninitiated
- Android的主要组件
- 2013.11.15 初学ant构建
- Hibernate入门之关系篇:多对一和一对多映射
- vs2012连接sql2008(错误类型:Could not load file or assembly)
- nginx服务器的基本配置
- 类型和原生函数及类型转换(三:终结js类型转换)
- jsp中静态include和动态include的区别
- 利用CNN神经网络实现手写数字mnist分类
- BigDecimal比较2个值是否相等,不能用equals,而要用compareTo
- PHP01
- WorkerMan 入门学习之(二)基础教程-Connection类的使用
- C#-MVC开发微信应用(5)--自动应答系统-自动回复机器人
- PHP里获取一维数组里的最大值和最小值
- java常见数据结构整理
- 对硬盘进行分区时,GPT和MBR有什么区别?
- Mongodb 笔记06 副本集的组成、从应用程序连接副本集、管理
- USACO 6.5 All Latin Squares