《Unix/Linux系统编程》第十周学习笔记
2024-09-08 14:16:02
《Unix/Linux系统编程》第十周学习笔记
块设备I/O和缓冲区管理
解释块设备I/O的原理和I/O缓冲的优点
I/O缓冲区:内核中的一系列NBUF缓冲区用作缓冲区缓存。每个缓冲区用一个结构体表示
typdef struct buf{
struct buf *next_free; //freelist pointer
struct buf *next_dev; //dev_list pointer
int dev,blk; //assigned disk block;
int opcode; //READ|WRITE
int dirty; //buffer data modified
int async; //ASYNC write flag
int valid; //buffer data valid
int busy; //buffer is in use
int wanted; //some process needs this buffer
struct, semaphore lock=l ; //buffer locking semaphore; value=L
struct semaphore iodone=0; //for process to wait for I/O completion;
char buf[BLKSIZE]; //block data area
} BUFFER;
BUFFER buf[NBUF], *freelist; // NBUF buffers and free buffer list
介绍Unix的缓冲区管理算法
I/O缓冲区:内核中的一系列NBUF 缓冲区用作缓冲区缓存。每个缓冲区用一个结构体表示。
typdef struct buf[
struct buf*next__free;// freelist pointer
struct buf *next__dev;// dev_list pointer int dev.,blk;
// assigmed disk block;int opcode;
// READ|wRITE int dirty;
// buffer data modified
int async;
// ASYNC write flag int valid;
//buffer data valid int buay;
// buffer is in use int wanted;
// some process needs this buffer struct semaphore lock=1; /
// buffer locking semaphore; value=1
struct semaphore iodone=0;// for process to wait for I/0 completion;// block data area char buf[BLKSIZE];)
} BUFFER;
BUFFER buf[NBUF],*freelist;// NBUF buffers and free buffer list
利用信号量设计新的缓冲区管理算法,以提高I/O缓冲区的缓存效率和性能
信号量的主要优点是:
(1)计数信号量可用来表示可用资源的数量,例如:空闲缓冲区的数量。
(2)当多个进程等待一个资源时,信号量上的V操作只会释放一个等待进程,该进程不必重试,因为它保证拥有资源。
使用信号量的缓冲区管理算法
1.保证数据一致性;
2.良好的缓存效果;
3.高效率:没有重试循环,没有不必要的进程“唤醒”
4.无死锁和饥饿。
介绍简单的PV算法及其特点
PV算法
BUFFER *getb1k(dev,blk):
while(1){
(1). P(free);
//get a free buffer first
if (bp in dev_1ist){
(2). if (bp not BUSY){
remove bp from freelist;P(bp);
// lock bp but does not wait
(3).return bp;
// bp in cache but BUSY V(free);
// give up the free buffer
(4).P(bp);
// wait in bp queue
return bp;v
// bp not in cache,try to create a bp=(dev,blk)
(5).bp = frist buffer taken out of freelist;P(bp);
// lock bp,no wait
(6).if(bp dirty){
awzite(bp);
// write bp out ASYNC,no wait
continue;
// continue from (1)
(7).reassign bp to(dev,blk);1/ mark bp data invalid,not dir return bp;-
// end of while(1);
brelse(BUFFER *bp),
{
(8).iF (bp queue has waiter)( V(bp); return; ]
(9).if(bp dirty && free queue has waiter){ awrite(bp);zeturn;}(10).enter bp into(tail of) freelist;V(bp);V(free);
}
实践内容
生产者消费者进程冲突问题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define N 100
#define true 1
#define producerNum 10
#define consumerNum 5
#define sleepTime 1000
typedef int semaphore;
typedef int item;
item buffer[N] = {0};
int in = 0;
int out = 0;
int proCount = 0;
semaphore mutex = 1, empty = N, full = 0, proCmutex = 1;
void * producer(void * a){
while(true){
while(proCmutex <= 0);
proCmutex--;
proCount++;
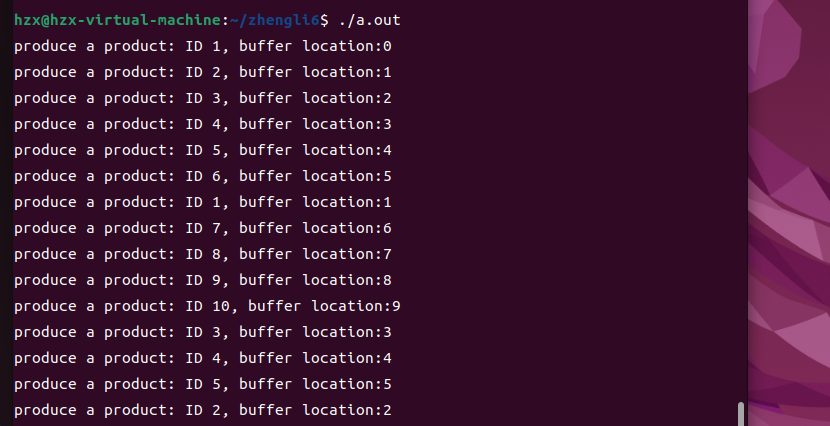
printf("produce a product: ID %d, buffer location:%d\n",proCount,in);
proCmutex++;
while(empty <= 0){
printf("buffer is full\n");
}
empty--;
while(mutex <= 0);
mutex--;
buffer[in] = proCount;
in = (in + 1) % N;
mutex++;
full++;
sleep(sleepTime);
}
}
void * consumer(void *b){
while(true){
while(full <= 0){
printf("buffer is empty\n");
}
full--;
while(mutex <= 0);
mutex--;
int nextc = buffer[out];
buffer[out] = 0;//消费完将缓冲区设置为0
out = (out + 1) % N;
mutex++;
empty++;
printf("produce a product: ID %d, buffer location:%d\n", nextc,out);
sleep(sleepTime);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t threadPool[producerNum+consumerNum];
int i;
for(i = 0; i < producerNum; i++){
pthread_t temp;
if(pthread_create(&temp, NULL, producer, NULL) == -1){
printf("ERROR, fail to create producer%d\n", i);
exit(1);
}
threadPool[i] = temp;
}//创建生产者进程放入线程池
for(i = 0; i < consumerNum; i++){
pthread_t temp;
if(pthread_create(&temp, NULL, consumer, NULL) == -1){
printf("ERROR, fail to create consumer%d\n", i);
exit(1);
}
threadPool[i+producerNum] = temp;
}//创建消费者进程放入线程池
void * result;
for(i = 0; i < producerNum+consumerNum; i++){
if(pthread_join(threadPool[i], &result) == -1){
printf("fail to recollect\n");
exit(1);
}
}//运行线程池
return 0;
}
最新文章
- 23种设计模式--代理模式-Proxy
- 【腾讯优测干货分享】安卓专项测试之GPU测试探索
- C# 的 Dictionary 寫入前應注意事項
- Ghost博客安装
- ASP.Net MVC开发基础学习笔记(4):校验、AJAX与过滤器
- [HIHO1052]基因工程(找规律)
- CUBRID学习笔记 11 数据类型之日期
- 20145305 《Java程序设计》实验四
- ACM2050
- CI中获取读操作的结果集行数+获取写操作的影响行数
- HDOJ的题目分类
- centos ldap
- gearman的安装和配置
- hdu_5963_朋友(找规律)
- python 内置函数 进制转换
- STM32L476应用开发之二:模拟量数据采集
- mysql系列八、mysql数据库优化、慢查询优化、执行计划分析
- 编程学习笔记(第四篇)面向对象技术高级课程:绪论-软件开发方法的演化与最新趋势(4)meta、元与元模型、软件方法的未来发展
- 有关索引的DMV
- 小白用Android MVP-初体验(一)