Java并发(十):读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock
先做总结:
1、为什么用读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock?
重入锁ReentrantLock是排他锁,在同一时刻仅有一个线程可以进行访问,但是在大多数场景下,大部分时间都是提供读服务,而写服务占有的时间较少。然而读服务不存在数据竞争问题,如果一个线程在读时禁止其他线程读势必会导致性能降低。所以就提供了读写锁。
读写锁维护着一对锁,一个读锁和一个写锁。通过分离读锁和写锁,使得并发性比一般的排他锁有了较大的提升:在同一时间可以允许多个读线程同时访问,但是在写线程访问时,所有读线程和写线程都会被阻塞。
2、读写锁实现原理:
(1)每个ReentrantReadWriteLock对象都对应着读锁和写锁两个锁。
(2)ReentrantReadWriteLock通过其属性sync(继承了AQS),一个对象实现了读写两个锁。
(3)sync.state(int)分为高 16 位和低16位,高16位用于共享模式ReadLock,低16位用于独占模式WriteLock
(4)获取写锁标志:
1.sync.state的低16位(0代表没有被占用,大于0代表有线程持有当前锁(锁可以重入,每次重入都+1) 最多2^16-1次重入
2.sync.exclusiveOwnerThread == Thread.currentThread()
(5)获取读锁标志:
1.state的高16位(0代表没有被占用,大于0代表有线程持有当前锁(锁可以重入,每次重入都+1) 最多2^16-1次重入
2.ThreadLocalHoldCounter readHolds; // 记录线程持有的读锁数量(ThreadLocalHoldCounter extends ThreadLocal)
readHolds.threadLocals - Map<ThreadLocal, HoldCounter>
HoldCounter - count tid
(关于ThreadLocal:Java并发(二十):线程本地变量ThreadLocal)
3.sync.cachedHoldCounter 记录最后一个获取读锁的线程的读锁重入次数,用于缓存提高性能
4.sync.firstReader 第一个获取读锁的线程(并且其未释放读锁),以及它持有的读锁数量 提高性能
(6)ReentrantReadWriteLock的内部类WriteLock/ReadLock通过操作sync的属性实现的锁的操作。
一、类结构
public class ReentrantReadWriteLock implements ReadWriteLock, java.io.Serializable {
// 属性
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readerLock;
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writerLock;
final Sync sync; // 锁
// 内部类
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {}
static final class FairSync extends Sync {}
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {}
public static class ReadLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {}
public static class WriteLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {}
}
二、读写锁实现
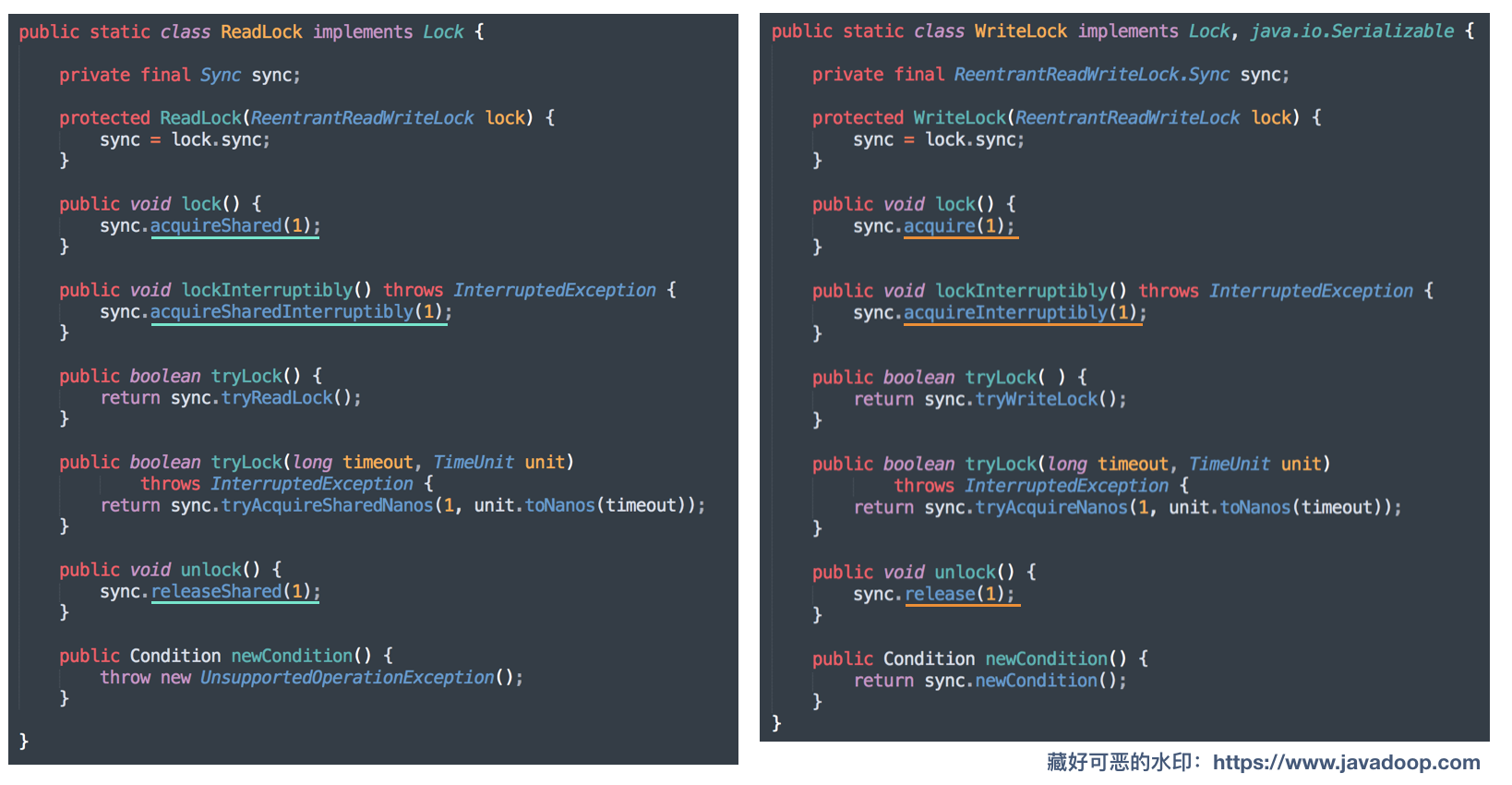
ReadLock 使用了共享模式,WriteLock 使用了独占模式。
ReadLock 和 WriteLock都是通过同一个Sync实例实现的。
AQS 将 state(int)分为高 16 位和低16位,高16位用于共享模式ReadLock,低16位用于独占模式WriteLock 。
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1; static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; } // 无符号补0右移16位 - 读锁
static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; } // 抹掉高16位 - 写锁
WriteLock:
1.state的低16位(0代表没有被占用,大于0代表有线程持有当前锁(锁可以重入,每次重入都+1) 最多2^16-1次重入
2.exclusiveOwnerThread == Thread.currentThread()
ReadLock:
1.state的高16位(0代表没有被占用,大于0代表有线程持有当前锁(锁可以重入,每次重入都+1) 最多2^16-1次重入
2.ThreadLocalHoldCounter readHolds; // 记录线程持有的读锁数量
readHolds.threadLocals - Map<Thread, HoldCounter>
HoldCounter - count tid
三、源码分析
写锁获取:
// ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock.lock()
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
} // AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquire(int)
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
} /**
* ReentrantReadWriteLock.Sync.tryAcquire(int)
* 可以获取写锁的两种情况:
* 1.没有线程占用该锁(读锁和写锁都没有被占用)
* 2.当前线程已经拿到过该写锁,重入
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c); // 写锁
if (c != 0) { // 有锁
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) // 有锁且没有写锁(即有读锁) || 其他线程占用了写锁
return false;
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT) // 重入锁上限 2^16-1
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
// 没有线程占用该锁,直接获取锁
if (writerShouldBlock() || // 如果是公平锁需要排队
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
写锁释放:
// ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock.unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
} // AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.release(int)
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
} /**
* ReentrantReadWriteLock.Sync.tryRelease(int)
* 释放写锁:维护state和exclusiveOwnerThread
*
*/
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int nextc = getState() - releases;
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
读锁
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
// 这个嵌套类的实例用来记录每个线程持有的读锁数量(读锁重入)
static final class HoldCounter {
int count = 0; // 持有的读锁数
final long tid = getThreadId(Thread.currentThread()); // 线程 id
}
static final class ThreadLocalHoldCounter extends ThreadLocal<HoldCounter> {
public HoldCounter initialValue() {
return new HoldCounter();
}
}
/**
* 组合使用上面两个类,用一个 ThreadLocal 来记录线程持有的读锁数量
*/
private transient ThreadLocalHoldCounter readHolds;
/**
* 用于缓存,记录最后一个获取读锁的线程的读锁重入次数
* 不管哪个线程获取到读锁后,就把这个值占为已用,这样就不用到 ThreadLocal 中查询 map 了
* 通常读锁的获取很快就会伴随着释放,在 获取->释放 读锁这段时间,如果没有其他线程获取读锁的话,此缓存就能帮助提高性能
*/
private transient HoldCounter cachedHoldCounter;
/**
* 第一个获取读锁的线程(并且其未释放读锁),以及它持有的读锁数量
* 提高性能用
*/
private transient Thread firstReader = null;
private transient int firstReaderHoldCount;
}
读锁获取:
// ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock.lock()
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
} // AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquireShared(int)
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
} /**
* ReentrantReadWriteLock.Sync.tryAcquireShared(int)
* 可以获取读锁情况:
* 1.没有线程占用该锁
* 2.只有读锁
* 3.有写锁,写锁被当前线程占用,锁降级
* 三种情况 - 只要没有其他线程占用写锁就可以获取读锁
*/
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) // 其他线程占用写锁
return -1;
int r = sharedCount(c); // 读锁
if (!readerShouldBlock() && r < MAX_COUNT && compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { // 进入此if,表示可以拿到读锁了
if (r == 0) { // 将"第一个"获取读锁的线程记录在firstReader属性中
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else { // 1.当前线程及对应读锁次数存入cachedHoldCounter 2.当前线程及对应读锁次数存入readHolds
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();// readHolds中取当先线程的ThreadLocal(没有就创建一个)
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);// 公平锁排队非公平锁下一个是写锁/读锁重入次数上限/CAS失败 重新拿读锁
} /**
* ReentrantReadWriteLock.Sync.fullTryAcquireShared(Thread)
*/
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) { // 循环CAS拿锁
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) // 其他线程占用写锁
return -1;
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) { // 处理读锁重入,将cachedHoldCounter设置为当前线程
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
} else {
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0) // 不是重入,返回-1
return -1;
}
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { // 正常拿读锁
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}
锁降级:
持有写锁的线程,去获取读锁的过程称为锁降级
读锁释放:
// ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock.unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
} // AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.releaseShared(int)
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
} /**
* ReentrantReadWriteLock.Sync.tryReleaseShared(int)
* 维护readHolds state
*/
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (firstReader == current) { // 第一个获取读锁的线程
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else { // readHolds中次数-1
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) { // state
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
参考资料 / 相关推荐
Java 读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 源码分析
【死磕Java并发】—–J.U.C之读写锁:ReentrantReadWriteLock
最新文章
- DotNet的JSON序列化与反序列化
- 树莓派系统介绍:DIetPi
- MFC的本质
- 支持ASP.NET WebService
- Mongodb常见错误
- 抽象工厂模式firstones
- QPointer更安全,QScopedPointer自动出范围就删除,QSharedDataPointer帮助实现隐式共享
- SpringMVC环境搭建---xml版及注解版
- Session 和 Cookie 区别
- How to change Eclipse loading image
- Windoes包管理工具(Scoop)
- Pandas Series和DataFrame的基本概念
- 机器学习技法笔记:08 Adaptive Boosting
- HDU - 1260 (Tickets)
- Linux架构分布式集群之基础篇
- 两个自定义对象List列表取交集(intersection)
- collections之deque【双向队列】与Queue【单向队列】
- 【转载】hadoop之failed task任务和killed task任务
- window.open居中显示
- BZOJ4299 Codechef FRBSUM(主席树)