Kilani and the Game CodeForces - 1105D (bfs)
Kilani is playing a game with his friends. This game can be represented as a grid of size n×mn×m, where each cell is either empty or blocked, and every player has one or more castles in some cells (there are no two castles in one cell).
The game is played in rounds. In each round players expand turn by turn: firstly, the first player expands, then the second player expands and so on. The expansion happens as follows: for each castle the player owns now, he tries to expand into the empty cells nearby. The player ii can expand from a cell with his castle to the empty cell if it's possible to reach it in at most sisi (where sisi is player's expansion speed) moves to the left, up, right or down without going through blocked cells or cells occupied by some other player's castle. The player examines the set of cells he can expand to and builds a castle in each of them at once. The turned is passed to the next player after that.
The game ends when no player can make a move. You are given the game field and speed of the expansion for each player. Kilani wants to know for each player how many cells he will control (have a castle their) after the game ends.
Input
The first line contains three integers nn, mm and pp (1≤n,m≤10001≤n,m≤1000, 1≤p≤91≤p≤9) — the size of the grid and the number of players.
The second line contains pp integers sisi (1≤s≤1091≤s≤109) — the speed of the expansion for every player.
The following nn lines describe the game grid. Each of them consists of mm symbols, where '.' denotes an empty cell, '#' denotes a blocked cell and digit xx (1≤x≤p1≤x≤p) denotes the castle owned by player xx.
It is guaranteed, that each player has at least one castle on the grid.
Output
Print pp integers — the number of cells controlled by each player after the game ends.
Examples
3 3 2
1 1
1..
...
..2
6 3
3 4 4
1 1 1 1
....
#...
1234
1 4 3 3
Note
The picture below show the game before it started, the game after the first round and game after the second round in the first example:
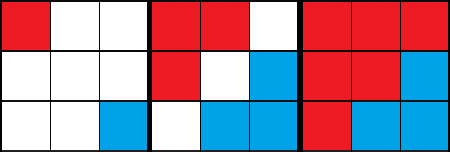
In the second example, the first player is "blocked" so he will not capture new cells for the entire game. All other player will expand up during the first two rounds and in the third round only the second player will move to the left.
题意:棋盘上有障碍物‘#’和‘.’和数字,每个数字有一个可以扩张的速度,数字一次扩张( 上下左右,可以转弯),一个'.'被占领了就不可以被占了,问最后的棋盘上的最终的数字的个数是多少
题解:差不多就是暴力bfs就可以了,记录一下什么先跑什么后跑就好了,一开始题意理解错了以为不可以转弯。
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1e3+; int n,m,t;
struct node{
int x,y,t;
};
int dx[]={,-,,};
int dy[]={,,,-};
int s[];
queue<node>q1[];
queue<node>q2[];
char map[maxn][maxn];
int vis[maxn][maxn]; int expand(int p)
{
int newx = ;
while(!q2[p].empty())
{
node x = q2[p].front();
q2[p].pop();
x.t = ; //此句话要与后面有句话连起来看,就是每次放进 q2[i] 队列的都要将步数为0
q1[p].push(x);
}
while(!q1[p].empty())
{
node x = q1[p].front();
q1[p].pop();
if (x.t == s[p])
{
q2[p].push(x); //如果已经满 s[p] 步,就将它重新放进 q1 的队列,并将步数归0
continue;
} for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
int xx = x.x + dx[i];
int yy = x.y + dy[i];
if(xx< || yy< || xx>n || yy>m || map[xx][yy]=='#' || vis[xx][yy] != || x.t+>s[p])
continue;
newx++;
q1[p].push(node{xx,yy,x.t+}); //步数+1
vis[xx][yy] = p; //记录棋盘
}
}
if(newx >= )
return ;
else
return ;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&t);
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
scanf("%d",&s[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j = ; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] >= '' && map[i][j] <= '')
{
vis[i][j] = map[i][j] - '';
q2[vis[i][j]].push(node{i,j,});
}
}
} while(true)
{
int flag = ;
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
flag += expand(i);
if(flag == )
break;
}
int count[];
memset(count,,sizeof count);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
count[vis[i][j]]++;
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
printf("%d ",count[i]);
}
/*
Input
3 3 2
1 1
1..
...
..2
Output
6 3
Input
3 4 4
1 1 1 1
....
#...
1234
Output
1 4 3 3
*/
最新文章
- 第二篇:Entity Framework CodeFirst & Model 映射
- angularjs(一)基础概念
- [JavaCore] 不错的Java基础学习资料-持续更新
- 移动端设备UA检测
- java 20 -1 递归的概述和案例
- 使用DbVisualizer 8 连接Oracle数据库
- AsyncTask 与 Thread+Handler
- createSQLQuery与createQuery的区别
- 手动配置Ubuntu Linux系列3-缺省网关和主机名
- leetcode面试准备:Reverse Words in a String
- 宝洁HR
- nignx开启expires后相关资源不显示的问题
- es6笔记1^_^let、string、number、math
- Xcode7.3.1中SKAudioNode在Scene转换后无声的问题
- java~springboot~目录索引
- COGS2187 [HZOI 2015] 帕秋莉的超级多项式
- mvc文件下载
- linux 一键安装lnmp环境
- Ansible批量更新远程主机用户密码 (包括Ansible批量做ssh互信)
- LaTeX :font size 修改字体大小的几种方式