面向对象_访问修饰符_构造与析构函数_this指针
2024-09-05 16:53:22
1:面向对象






以codeblocks举例,在一个工程里面: File-->new -->Class可以建一个类,可以设置类的参数,是否有set get方法,有无构造函数等设置,.h文件主要用来写类的属性和
方法声明,类名.cpp文件里面实现函数,main函数里面负责对象的调用和操作。
如下:Student.h
#ifndef STUDENT_H
#define STUDENT_H
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student();//构造函数,进行数据的初始化
Student(string name, int age);
virtual ~Student(); string Getname() { return name; }//对类的变量进行封装,便于对私有的属性进行操作
void Setname(string val) { name = val; }
int Getage() { return age; }
void Setage(int val) { age = val; }
int* Getscore() { return score; }
void Setscore(int* val) { score = val; }
void Show(string , int );//在.h文件里面进行函数定义
protected: private://私有的属性
string name;
int age;
int* score;
}; #endif // STUDENT_H
main.cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
#include "Student.h"
int main()
{
Student stu1;//;自动调用无参构造函数
cout << "由构造函数初始化的年龄和姓名" <<stu1.Getage() << stu1.Getname() << endl;
Student stu2("小红",12);//有参构造函数
stu1.Show("小明",13);
return 0;
}
student.cpp
/*
* 文件名:
* 描 述:
* 作 者:
* 时 间:
* 版 权:
*/#include "Student.h"
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
Student::Student()
{
name = "默认名";
age = 100;
cout << "我是(无参)构造函数" << endl;
}
Student::Student(string name,int age){
Student::Setage(age);
Student::Setname(name);
name = Student::Getname();
age = Student::Getage();
cout << "学生" <<name<< "的年龄是" << age << endl;
} Student::~Student()
{
cout << "我是析构函数,负责对象的回收" << endl;
}
void Student::Show(string name, int age)
{
cout << "学生" <<name << "的年龄是" << age << endl;
}
2:访问修饰符

通过为参数设置set和get方法进行私有属性的操作。
#ifndef STUDENT_H
#define STUDENT_H
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student();//构造函数,进行数据的初始化
Student(string name, int age);
virtual ~Student(); string Getname() { return name; }//对类的变量进行封装,便于对私有的属性进行操作
void Setname(string val) { name = val; }
int Getage() { return age; }
void Setage(int val) { age = val; }
int* Getscore() { return score; }
void Setscore(int* val) { score = val; }
void Show(string , int );//在.h文件里面进行函数定义
protected: private://私有的属性
string name;
int age;
int* score;
}; #endif // STUDENT_H
3:构造与析构函数

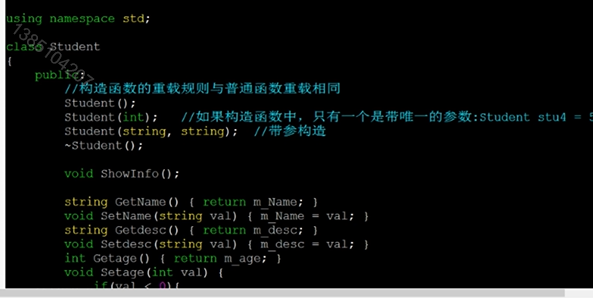


.cpp文件
/*
* 文件名:
* 描 述:
* 作 者:
* 时 间:
* 版 权:
*/#include "Student.h"
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
Student::Student()
{
name = "默认名";
age = ;
cout << "我是(无参)构造函数" << endl;
}
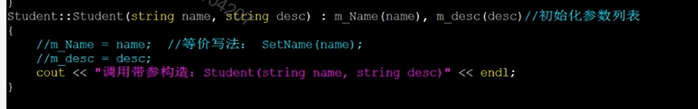
Student::Student(string name1,int age1):name(name1),age(age1)//初始化列表
{
//name = name1;
//age = age1;
name = Student::Getname();
age = Student::Getage();
cout << "学生" <<name<< "的年龄是" << age << endl;
} Student::~Student()
{ cout << "我是析构函数,负责对象"<< Student::Getname()<<"的回收" << endl;
}
void Student::Show(string name, int age)
{
cout << "学生" <<name << "的年龄是" << age << endl;
}
main.cpp文件
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
#include "Student.h"
int main()
{
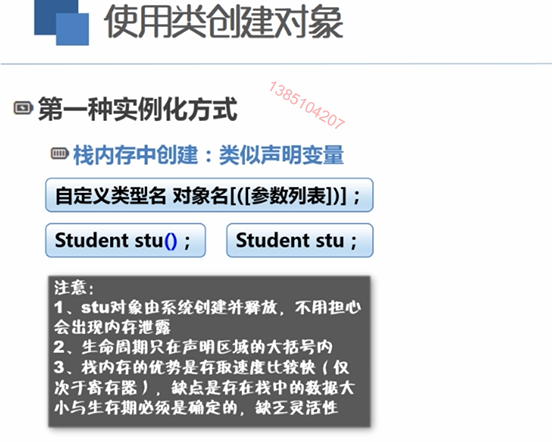
Student stu1;//;自动调用无参构造函数,在栈内存中分配空间,自动调用delete回收
cout << "由构造函数初始化的年龄和姓名" <<stu1.Getage() << stu1.Getname() << endl;
Student stu2("小红",);//有参构造函数
stu1.Show("小明",); Student* stu3 = new Student("岳飞",);//在堆空间中分配内存
cout << "名字是" << stu3->Getname() << endl;
delete stu3;//需要手动调用delete释放内存 return ;
}

栈空间对象自动释放,通过new占用的堆空间需手工delete释放,析构函数只有一个,不能重载。
4:this指针

(*this)返回的是类对象本身。
最新文章
- 【SQL篇章--DATABASE/EVENTS】
- webpack模块依赖管理介绍
- Lua 之数据结构
- YHLMR009 交货单查询
- 使用adb shell dumpsys检测Android的Activity任务栈
- 【转载】Android异步处理系列文章
- 【转贴】Linux系统NGINX负载均衡404错误处理方法
- 剑指offer--面试题6
- jQuery的遍历方法
- jquery css hover
- Linux的环境变量
- Redis基础学习(二)—数据类型
- 如何在openlayer接入矢量数据
- Python 之ConfigParser模块
- 【395】yield 和 yield from
- Vuejs——(10)组件——父子组件通信
- React Native常用组件之ScrollView
- ipv6禁用导致rpcbind服务启动失败解决办法
- LeetCode 104 Maximum Depth of Binary Tree 解题报告
- Linux学习 :多线程编程