如何在Spring Boot 中动态设定与执行定时任务
本篇文章的目的是记录并实现在Spring Boot中,动态设定与执行定时任务。
我的开发项目是 Maven 项目,所以首先需要在 pom.xml 文件中加入相关的依赖。依赖代码如下所示:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.quartz-scheduler</groupId>
<artifactId>quartz</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
下图是定时任务的列表及功能展示。
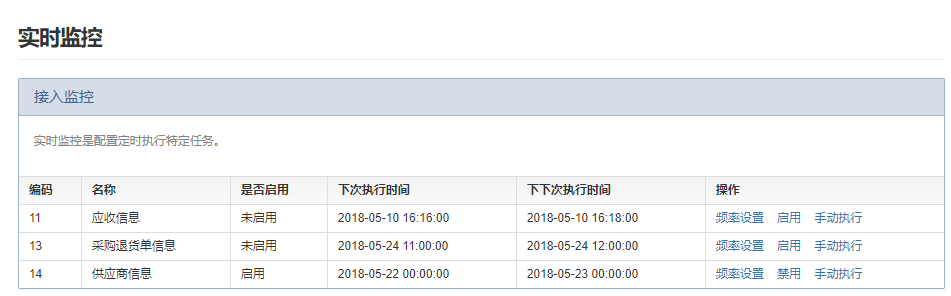
一般情况下,定时任务列表都是初始化生成,所以此处并无定时任务的新增功能。每个定时任务的操作栏中都有三种操作,分别是 频率设置、启用(禁用)、手动执行。
频率设置:设置定时任务的执行频率,设置成功后,可以重新设置定时任务的执行频率,这个功能是动态设定执行频率的保证。
启用(禁用):控制定时任务的执行状态,定时执行或者不执行。启用前,需先设置定时任务的执行频率。
手动执行:手动调用定时任务的执行方法,无需等到下次执行时间。手动执行前,定时任务的状态应该为启用状态。

在执行频率的设定上,我选择了直接使用Cron表达式,为了简单与方便,我在末端小图标上加了一个链接,点击图标后,便会跳转到在线Cron表达式页面。
<div class="row">
<label class="label col col-3 text-align-right">频率设置<font color="red">*</font>:</label>
<div class="col col-8">
<div class="input-group ">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="cron" name="cron" th:value="${monitor.cron}" placeholder="点击末端小图标在线获取Cron表达式"/>
<span onclick="getCron()" class="input-group-addon"><i class="fa fa-calendar"></i></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
//在线获取Cron表达式
function getCron() {
window.open("http://cron.qqe2.com/"); //打开一个新的网页,不会覆盖当前网页
}
在新打开的网页上,根据需求设定执行频率,将生成的Cron表达式复制到文本框中,点击 “确定” 按钮。下面的代码是点击 “确定” 按钮后,后台的处理逻辑。
@RequestMapping(value = "setFrequencyCron", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
@OperationLog(success = "设置频率成功", failure = "设置频率失败")
public Json setFrequencyCron(Monitor monitor) {
try {
Monitor m=monitorService.getMonitorById(monitor.getId());
m.setCron(monitor.getCron());
CronSequenceGenerator cronSequenceGenerator = new CronSequenceGenerator(monitor.getCron());
Date currentTime = new Date(); //当前系统时间
Date nextTimePoint = cronSequenceGenerator.next(currentTime); //下次执行时间
Date nextNextTimePoint = cronSequenceGenerator.next(nextTimePoint); //下下次执行时间
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String nextTime=sdf.format(nextTimePoint);
String nextDoubleTme=sdf.format(nextNextTimePoint);
m.setNextTime(nextTime);
m.setNextDoubleTime(nextDoubleTme);
m.setEnable("0"); //设置频率,让其状态变为“禁用”
monitorService.updateMonitor(m);
return Json.ok("频率设置成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("频率设置失败: " + e.getMessage(), e);
return Json.fail("频率设置失败");
}
}
根据Cron表达式,使用 Spring 自带的 CronSequenceGenerator 类可以获得下次执行时间和下下次执行时间。每次设定新的执行频率后,该定时任务的状态都会变为“禁用”,需要重新启用,定时任务才能生效。
下面的代码是点击 “启用”或“禁用” 按钮后,后台的处理逻辑。
@RequestMapping(value = "setEnable", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
@ResponseBody
@OperationLog(success = "操作成功", failure = "操作失败")
public Json setEnable(Long id, String enable) {
Json json=new Json();
try {
String msg="";
Monitor monitor=monitorService.getMonitorById(id);
monitor.setEnable(enable);
monitorService.updateMonitor(monitor);
if (enable.equals("1")){
msg="启用成功";
}else if (enable.equals("0")){
msg="禁用成功";
}
//启用或禁用时,清空redis中的监控信息
redisUtils.remove(KEY);
json.setMsg(msg);
json.setSuccess(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return Json.fail("操作失败");
}
return json;
}
在定时任务的执行过程中,为了减少与数据库的交互,所以使用了缓存工具类 RedisUtils ,会将最新的定时任务信息保存到 RedisUtils 中。所以在启用与禁用定时任务时,将会清除以前保存在 RedisUtils 中的定时任务信息,加载最新的定时任务信息。
在启动类的上方加上 @EnableScheduling 注解,该注解的作用是开启Spring Boot对定时任务的支持。
@EnableScheduling
public class DueUIApplication extends AbstractStdApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DueUIApplication.class, args);
} }
新建一个定时任务执行类 MonitorTask ,在该类中加一个用于扫描定时任务的方法,在该方法上方需要加上 @Scheduled 注解,同时需要带上参数,设定扫描频率。
代码如下所示:
@Component
public class MonitorTask extends AbstractStdAction {
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(MonitorTask.class); @Autowired
private MonitorService monitorService; private String KEY="pbeechina:due:ui:monitor:action"; //redis的key /**
* 每隔一分钟秒扫描一次监控信息
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0/1 * * * ? ")
@Transactional(propagation= Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED) //不需要事物管理
public void scanMonitor(){
try {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("**********开始扫描监控的定时任务***********");
} List<Monitor> monitorList=null; //预警监控信息 boolean isKey=redisUtils.exists(KEY); //判断key值是否存在
if (isKey){ //key存在,代表监控信息是最新的
monitorList=(List<Monitor>)redisUtils.get(KEY);
}else {
monitorList=monitorService.getMonitorList(); //查询所有已被启用的监控
if (monitorList != null && monitorList.size() > 0){
redisUtils.set(KEY,monitorList, 1,TimeUnit.DAYS); //设置过期时间一天
}
} if (monitorList != null && monitorList.size() > 0){
for (Monitor monitor:monitorList){
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(monitor.getCron())){
CronExpression expression = new CronExpression(monitor.getCron());
if(expression.isSatisfiedBy(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()))){
LOGGER.info("开始执行定时任务...");
monitorService.autoExecute(monitor);
}
}
}
} if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("*******扫描结束***********");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("监控定时任务扫描失败", e);
}
}
}
至此,Spring Boot动态执行定时任务的功能就实现了。
最新文章
- IE浏览器不能访问网页,google可以访问
- CentOS6.5 安装 jdk1.7
- isDebugEnabled作用
- HDU 2089 不要62(数位DP)
- python自动化执行脚本
- vs中动态DLL与静态LIB工程中加入版本信息的方法
- cocos2d-x3.2中map的基本操作和使用
- 【.NET】转载:使用FileStream批量上传文件。
- 《JavaScript高级程序设计》笔记:使用Canvas绘图(15)
- CentOS 7下给nginx安装SSL证书
- UBB编辑器
- SoapUI Pro Project Solution Collection-Custom project and setup
- java再次学习
- Java中static、final、static final的区别(转)+transient
- ios开发周期之--(向上,向下,四舍五入)取整
- TF随笔-12
- LeetCode 275. H-Index II
- javascript总结37:DOM:innerText 和 innerHTML
- Ubuntu 中QT 用sogou拼音 安装
- SpringBoot MockMVC