about how to determine a prime number
(1) if divided by 2 or 3, then no;
(2) we only have to go through prime factors; because a composite can always be divided into primes.
(3) since 2 is the smallest prime, for number N, we only have to go through till N/2 max., because if one number is not a prime, the other factor must be no less than 2;
(4) consider N=n*m. If n<sqrt( N ), then it’s a must that m>sqrt( N ). So we only have to go through till sqrt( N )+1 max., because if there’s not a factor with in [2, sqrt(N)+1], there wouldn’t be one above;
(5) other than 2 and 3, prime numbers trend to have a format of (6n +/- 1), but not vise versa.
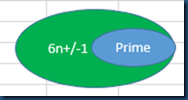
Now, I haven’t seen a strick mathematical prove on that theory, but someone has run a promgram certifying that at least the first 1 million prime numbers fit in that conclusion.
So if the number is not insanely big, it’s true.
That being say, if we divide a number by (6n +/- 1), it would include many non-prime dividers of course, but we are able to cover all prime factors, too.
Followed is one example:
l = (int) Math.sqrt (n) + 1;
for (i=6; i<=l; i+=6) {
if (n % (i + 1) == 0) return false;
if (n % (i - 1) == 0) return false;
}
// must be prime
(6) seive of Eratosthenes
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/%E5%9F%83%E6%8B%89%E6%89%98%E6%96%AF%E7%89%B9%E5%B0%BC%E7%AD%9B%E6%B3%95
The running time for this algorithm is: O = nlog(logn).A pseudo code as followed:
Input: an integer n > 1 Let A be an array of Boolean values, indexed by integers 2 to n,
initially all set to true. for i = 2, 3, 4, ..., not exceeding √n:
if A[i] is true:
for j = i2, i2+i, i2+2i, i2+3i, ..., not exceeding n :
A[j] := false Output: all i such that A[i] is true.
Use seive of Eratosthenes would greatly improve the screening speed. Followed is one example:
public static void main (String args[]) {
int i, j, l;
A = new boolean[N+1];
// do a sieve of Eratosthenes
for (i=0; i<=N; i++) A[i] = true;
l = (int) Math.sqrt (N);
// for each number i from 2 to square root of N...
for (i=2; i<=l; i++)
// ...mark off all the multiples of i
for (j=i*i; j<=N; j+=i) A[j] = false;
// count whatever is left; these are all the primes
for (i=2,j=0; i<=N; i++) if (A[i]) j++;
System.out.println (j);
}
最新文章
- node.js学习总结(一)
- Java 浅析三大特性之一多态
- Java基础--反射机制的知识点梳理
- 在oracle中通过connect by prior来实现递归查询!
- ASP.NET MVC图片管理(上传,预览与显示)
- iOS开发网络请求——大文件的多线程断点下载
- angularjs发送delete请求传参数的方法
- Unity3D手游开发日记(8) - 运动残影效果
- jQueryEasyUI
- 关于FireMonkey TGrid赋值的一点小研究
- (11)lambda表达式用法
- LabView调用C#混合模式dll
- 《PHP扩展开发及内核应用》
- 调用API函数,在窗口非客户区绘图(通过GetWindowDC获得整个窗口的DC,就可以随意作画了)
- 单选按钮、复选按钮——axure线框图部件库介绍
- Codeforces 107B Basketball Team 简单概率
- synchronized的使用及注意事项
- Tornado框架简介
- JS for循环 if判断、white循环。小练习二
- Celery结合Django使用