[Python自学] day-21 (2) (Cookie、FBV|CBV装饰器)
一、什么是Cookie
1.什么是Cookie?
Cookie是保存在客户端浏览器中的文件,其中记录了服务器让浏览器记录的一些键值对(类似字典)。
当Cookie中存在数据时,浏览器在访问网站时会读取属于自己的数据,并携带在请求中发送给服务器。
这种机制可以用于许多场景,例如用户登录。
Cookie非常重要,如果禁用了Cookie,大部分网站都不好用。
2.如何禁用Cookie
以Chrome为例:
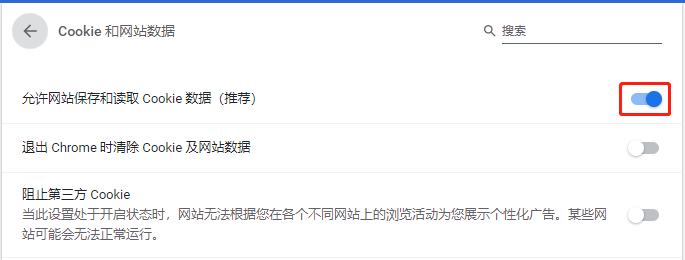
进入设置--->高级--->隐私设置与安全性--->网站设置(或内容设置)--->Cookie和网站数据--->允许网站保存和读取Cookie数据(关闭)
3.关闭Cookie尝试登陆JD
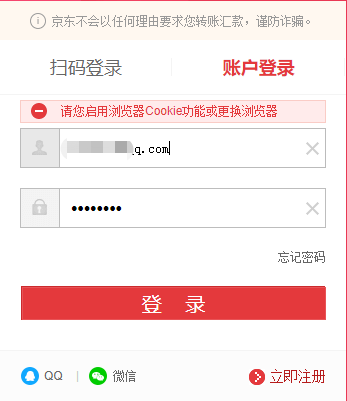
在没有Cookie的情况下,会被提示"请再次登陆"或者"请您启用浏览器Cookie功能或更换浏览器"。
二、基于Cookie实现用户登录
1.实现登录页面mlogin.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Mgmt Login</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/commons.css"/>
<style>
label{
width: 80px;
text-align: right;
display: inline-block;
}
.error_span{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body class="common">
<form action="/mgmt/login/" method="post">
<p>
<label for="username">用户名:</label>
<input id="username" type="text" name="user"/>
<span class="error_span">{{ user_error }}</span>
</p>
<p>
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input id="password" type="password" name="pwd"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
<span class="error_span">{{ pwd_error }}</span>
</p>
</form>
<script src="/static/jquery-1.12.4.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
2.实现视图函数login()
def login(request):
pwd_error_msg = ''
# 当用户使用GET请求时,让其登录
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, 'mlogin.html')
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get('user', None)
password = request.POST.get('pwd', None)
dic = user_info.get(username)
if not dic:
# 用户不存在,重新登录
pwd_error_msg = "用户不存在"
return render(request, 'mlogin.html', {"pwd_error": pwd_error_msg})
if dic['pwd'] == password:
response = redirect('/mgmt/host')
response.set_cookie('username', username)
return response
else:
# 密码不正确,重新登录
pwd_error_msg = "密码不正确"
return render(request, 'mlogin.html', {"pwd_error": pwd_error_msg})
当账号密码验证成功时,向客户端写入cookie,并跳转到/mgmt/host页面。
3.定义映射关系
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.urls import re_path from mgmt import views app_name = 'mgmt'
urlpatterns = [
path('index/', views.index),
re_path('host', views.host),
re_path('login', views.login),
]
4.在host()视图函数中验证cookie
def host(request):
# 如果是get请求,则将数据库中查询到的host列表和业务线列表返回,展示在页面上
if request.method == 'GET':
username = request.COOKIES.get('username')
if not username:
return redirect('/mgmt/login')
host_list = models.Host.objects.all()
busi_list = models.Business.objects.all()
return render(request, 'host.html', {'username': username, 'host_list': host_list, 'busi_list': busi_list})
elif request.method == 'POST': # 当用户使用模态框添加主机时,使用表单POST提交
# 获取表单提交的数据
host = request.POST.get('hostname')
ip = request.POST.get('ip')
port = request.POST.get('port')
# 这里的busi获取到的是select对应的busi_id
busi = request.POST.get('busi_id')
# 插入数据库
models.Host.objects.create(
hostname=host,
ip=ip,
port=port,
busi_id=busi
)
# 重定向到host页面,以GET重新请求,页面就可以显示新的值
return redirect('/mgmt/host')
如果没有cookie,则说明没有登录,跳转回login页面。如果有cookie,则显示登录用户名。
/mgmt/host页面的html代码和models代码参考:[Python自学] day-20 (Django-ORM、Ajax)
三、Cookie参数
1.Cookie失效时间
我们如果使用set_cookie('key',value)来设置Cookie,则Cookie会在关闭浏览器时失效。
有两种方式设置失效时间:
1)max_age参数(单位秒)
set_cookie('username', username, max_age=10)
这样设置以后,Cookie的有效时间就是10s,10s后刷新页面,就会跳转到登录页面(前提是写了这个跳转逻辑)。
2)expires参数(参数为datetime)
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.utcnow()
delay = datetime.timedelta(10)
response.set_cookie('username', username, expires= now+delay)
同样设置以后,有效时间也是10s。
2.Cookie path、domain、secure、httponly参数
path参数:
当我们按前面章节的代码来添加Cookie的时候,Cookie是在所有页面都能访问的。
但是我们有可能需要在不同的页面访问不同的Cookie值,例如论坛的两个页面,一个页面(host页面)设置一页显示50条数据,另外一个页面(app)设置一页显示20条数据。
使用path参数:
set_cookie('show_num', 50, path='/') # 所有页面
set_cookie('show_num', 50, path='/host') # Host页面一页显示50条数据
set_cookie('show_num', 20, path='/app') # App页面一页显示20条数据
domain参数:
用于设置cookie生效的域名。用于过滤生效范围。
secure参数:
如果使用的是https协议,则secure必须设置为Ture。
httponly参数:
如果httponly=True,则表示Cookie只能通过http协议传输,无法被JavaScript获取(不是绝对的,底层抓包可以获取到也可以被覆盖)
如果不设置,则在前端JS代码中可以使用以下代码获取cookie:
console.log(document.cookie) //"username=leokale"
四、Cookie实现动态调整每页显示条目数
在 [Python自学] day-21 (1) (请求信息、html模板继承与导入、自定义模板函数、自定义分页) 中,我们实现了分页功能。效果如下:
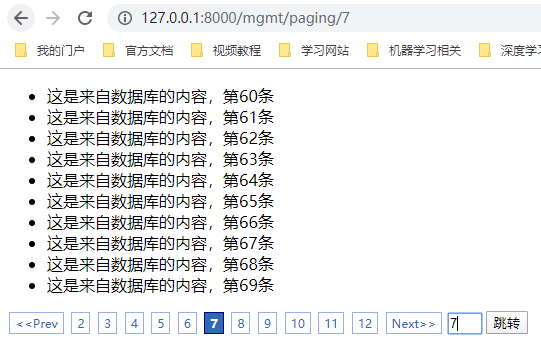
每页默认显示10条数据。我们可以使用Cookie来实现动态调整每页显示条目数量。
1.在html中添加一个<select>标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Paging</title>
<style>
/*分别定义页签按钮的效果,以及当前页面的页签按钮效果*/
.pagination{
font-size: 12px;
/*一般页签按钮都居中*/
/*text-align: center;*/
}
.pagination .page_num{
display: inline-block;
padding: 2px 5px;
border: 1px solid #9aafe5;
color: #2e6ab1;
margin: 0 2px;
text-decoration: none;
}
.pagination .page_num.active{
background-color: #2e6ab1;
border: 1px solid #000080;
color: #fff;
font-weight: bold;
margin: 0 2px;
padding: 2px 5px;
}
a{
outline: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 显示内容 -->
<ul>
{% for text in contents %}
<li>
{{ text }}
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<select id="select_page_show_num"onchange="changePageShowNum(this);">
<option value="10">10</option>
<option value="30">30</option>
<option value="50">50</option>
<option value="100">100</option>
</select>
<!-- 显示页签按钮 -->
<div class="pagination">
{{ paginations }}
</div>
<script src="/static/jquery-1.12.4.js"></script>
<script src="/static/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
<script>
// 页面加载完后,马上读取cookie的值,设置在select框中
$(function(){
var v = $.cookie('per_page_count');
if(!v){
v = '';
}
$("#select_page_show_num").val(v)
});
//当用户选择select标签中的值后,设置cookie
function changePageShowNum(ths){
var v = $(ths).val();
$.cookie('per_page_count',v);
location.reload();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
解释:
1)导入jquery cookie插件,为jquery添加便利操作cookie的功能。下载地址 https://plugins.jquery.com/cookie/
2)添加一个<select>标签,提供用户每页显示数目的功能。
3)当页面加载完毕的时候,读取cookie是否存在per_page_count的值,如果没有,则默认为10,如果有,则设置在select标签中,确保显示与cookie一致。
4)当用户改变<select>的选项时,动态的将值写入per_page_count中。
2.修改paging()视图函数
def paging(request, pnum):
# 从请求中,获取Cookie per_page_count的值
ppc = request.COOKIES.get('per_page_count')
# 将值转换为int类型,并将其作为参数传入Paging构造函数
ppc = int(ppc)
# 获取一个分页对象
pager_obj = Paging(pnum, len(PAGES), per_page_count=ppc)
# 获取页签按钮的list
paginations = pager_obj.pager_str('/mgmt/paging/')
# 根据start和end来获取数据,对应数据库的行数
contents = PAGES[pager_obj.start_idx: pager_obj.end_idx] return render(request, 'paging.html', {"contents": contents, "paginations": paginations})
3.实现效果
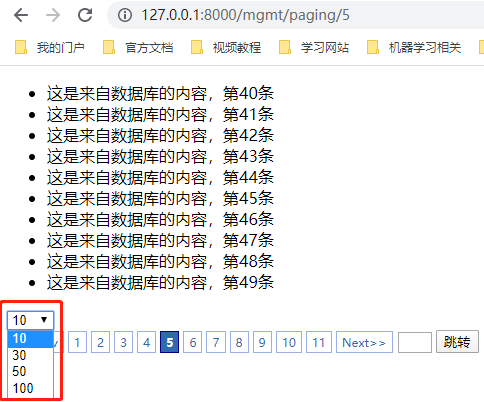
五、带签名的Cookie(加密)
普通设置的Cookie都是明文的,如果我们想对cookie进行加密,则使用以下方式:
set_signed_cookie('username', username, salt='nsakjdf98s7dfhsf')
get_signed_cookie('username', salt='nsakjdf98s7dfhsf')
通过使用加盐的方式来加密,salt在设置cookie和获取cookie的时候一定要对应上。
六、使用装饰器实现用户验证
1.FBV装饰器
如果我们在很多页面的视图函数都要验证用户是否登录(验证是否存在指定Cookie),则需要在每个视图函数中写以下代码:
username = request.COOKIES.get('username')
if not username:
return redirect('/mgmt/login')
如果使用装饰器,则实现为:
# 实现用户登录cookie验证的装饰器
def auth(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
username = request.COOKIES.get('username')
if not username:
return redirect('/mgmt/login')
return func(request, *args, **kwargs) return inner
2.CBV装饰器
当使用的是CBV的请求处理方式,里面的get、post方法都是分开的,如果我们为每一个函数都添加auth装饰器,比较麻烦。
django为我们提供了一个封装好的装饰器容器。
使用方法一(麻烦,不推荐):为每一个函数加上装饰器
from django import views
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator # 实现用户登录cookie验证的装饰器
def auth(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
username = request.COOKIES.get('username')
if not username:
return redirect('/mgmt/login')
return func(request, *args, **kwargs) return inner class Host(views.View):
@method_decorator(auth)
def get(self, request):
username = request.COOKIES.get('username')
# 如果是get请求,则将数据库中查询到的host列表和业务线列表返回,展示在页面上
if request.method == 'GET':
host_list = models.Host.objects.all()
busi_list = models.Business.objects.all()
return render(request, 'host.html', {'username': username, 'host_list': host_list, 'busi_list': busi_list}) @method_decorator(auth)
def post(self, request):
# 获取表单提交的数据
host = request.POST.get('hostname')
ip = request.POST.get('ip')
port = request.POST.get('port')
# 这里的busi获取到的是select对应的busi_id
busi = request.POST.get('busi_id')
# 插入数据库
models.Host.objects.create(
hostname=host,
ip=ip,
port=port,
busi_id=busi
)
# 重定向到host页面,以GET重新请求,页面就可以显示新的值
return redirect('/mgmt/host')
使用方法二(麻烦):利用dispatch方法先于get、post方法执行。
from django import views
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator # 实现用户登录cookie验证的装饰器
def auth(func):
#...... class Host(views.View):
@method_decorator(auth)
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super(Host, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) def get(self, request):
#...... def post(self, request):
#......
由于dispatch方法先于get、post方法执行,所以在这里统一做验证就可以。
使用方法三(推荐):在类上加装饰器。
from django import views
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator # 实现用户登录cookie验证的装饰器
def auth(func):
#...... @method_decorator(auth, name='dispatch')
class Host(views.View):
def get(self, request):
#...... def post(self, request):
#......
在类前面加装饰器,并使用name参数指定成员方法名,相当于第二种使用方法。
最新文章
- echarts之tooltip-position
- jQuery鼠标经过显示大图
- Android源码中内置包含so文件的APK文件
- 一次Redis的使用Bug记录(exec)
- [No00001E]不出国,学口语-出国口语自然好?才怪咧!
- Realm Java的学习、应用、总结
- SpringMvc+Mybatis 框架搭建
- led.c驱动框架
- 彻底领悟javascript中的this
- WP8.1小梦词典开发1:金山词霸API使用
- 代码的鲁棒性:链表中倒数第k个结点
- 第一节: dingo/API 最新版 V2.0 之安装讲解(连载)
- ActiveMQ的Destination高级特性
- layer结合art实现弹出功能
- Python_oldboy_自动化运维之路_面向对象2(十)
- 循环结构 while,do while
- 【js】插件—动效Velocity.js
- POJ 3579 Median 二分加判断
- PHP 中使用explode()函数切割字符串为数组
- 3人从小公寓创业,到世界最大引擎公司,Unity创始人谈14年...