Navicat 软件的使用以及pymysql
2024-09-01 20:42:45
Navicat 软件的使用以及pymysql
一、navicate的安装及使用
下载
直接百度搜索navicate ,如下图

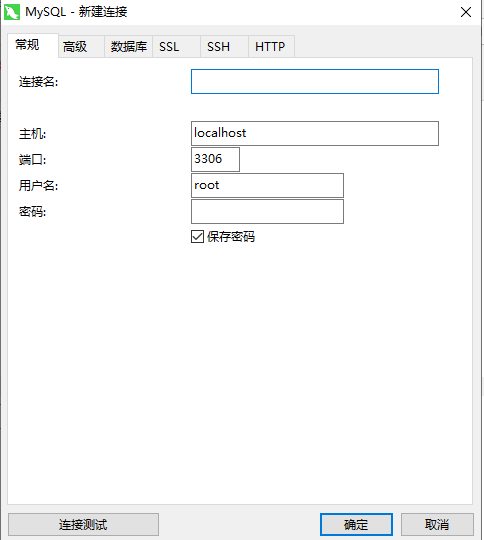
连接数据库
新建数据库以及新建表
选中然后鼠标右键
- 建模


- 利用navicate去查询练习
-- 查询所有的课程的名称以及对应的任课老师的姓名
-- SELECT
-- course.cname,
-- teacher.tname
-- FROM
-- course
-- INNER JOIN teacher ON course.teacher_id = teacher.tid;

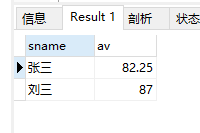
-- 查询平均成绩大于80分的同学的姓名和平均成绩
SELECT
student.sname,
t1.av
FROM
student
INNER JOIN (
SELECT
score.student_id,
avg( score.num ) AS av
FROM
score
GROUP BY
score.student_id
HAVING
avg( score.num ) > 80
) AS t1 ON student.sid = t1.student_id;
-- 查询没有同时报李平老师课的学生姓名
-- 1、查李平老师教授的课程id
-- 2、去score表中查询报了李平老师课程的学生id
-- 3、再去学生表中查学生的姓名
SELECT
*
FROM
student
WHERE
student.sid NOT IN (
SELECT DISTINCT
score.student_id
FROM
score
WHERE
score.course_id IN ( SELECT course.cid FROM course INNER JOIN teacher ON course.teacher_id = teacher.tid WHERE teacher.tname = '李平老师' )
);

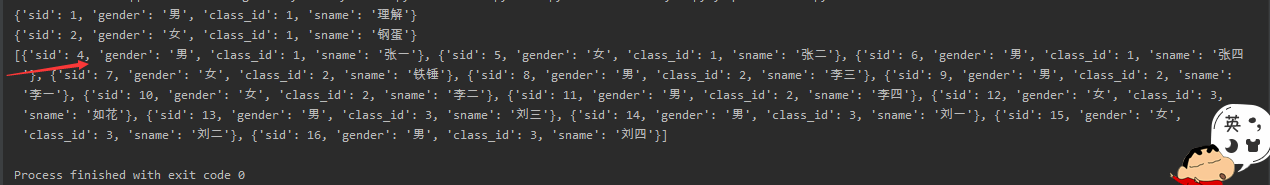
查询没有同时选修物理课程和体育课题的学生姓名(只能在两者间选一门)
-- 1、先查询物理以及体育的id号
#2、先拿到所有报了物理、体育的学生的id
SELECT
student.sname
FROM
student
WHERE
student.sid IN (
SELECT
score.student_id
FROM
score
WHERE
score.course_id IN ( SELECT course.cid FROM course WHERE course.cname IN ( '物理', '体育' ) )
GROUP BY
score.student_id
HAVING
COUNT( score.course_id ) = 1
);
-- 查询挂科超过两门(包括两门)的学生姓名和班级
# 1、先拿所有分数小于60的
SELECT
student.sname,
class.caption
FROM
student
INNER JOIN class ON student.class_id = class.cid
WHERE
student.sid IN ( SELECT score.student_id FROM score WHERE num < 60 GROUP BY score.student_id HAVING count( score.course_id ) >= 2 );
二、pymysql
- 初识
import pymysql
coon = pymysql.connect(
user = 'root',
password = '123456',
host = '127.0.0.1',
port = 3306,
charset = 'utf8',
database = 'day36_1'
)
cursor = coon.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 产生了一个游标对象
# cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor 将查询出来的结果制作成字典的形式返回
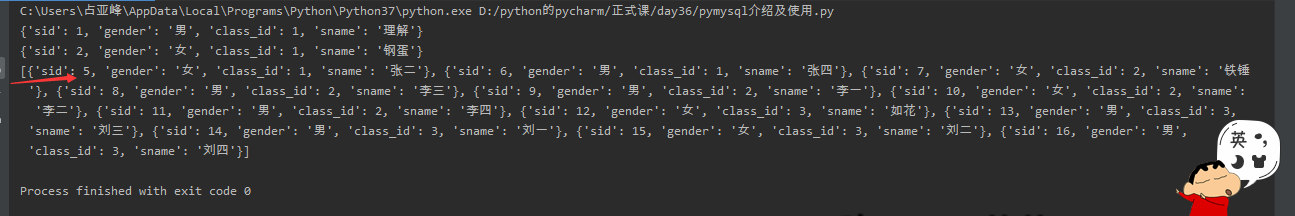
sql = 'select * from student'
res = cursor.execute(sql) # 执行sql语句
# print(res) # execute返回的是当前SQL受影响的行数
# ret = cursor.fetchone() # 只获取查询结果中的一条数据
# ret = cursor.fetchall() # 获取查询结果中的所有数据
# ret = cursor.fetmany() # 指定获取几条数据 如果数字超了也不会报错
# print(ret)
print(cursor.fetchone())
print(cursor.fetchone())
# 相对移动
cursor.scroll(2, 'relative') # 基于指针所在的位置 往后偏移
# 绝对移动
# cursor.scroll(3, 'absolute') # 基于起始位置 往后偏移
print(cursor.fetchall())
相对移动
绝对移动
- sql注入问题
import pymysql
coon = pymysql.connect(
user = 'root',
password = '123456',
db = 'day36_1',
host = '127.0.0.1',
port = 3306,
charset = 'utf8'
)
cursor = coon.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
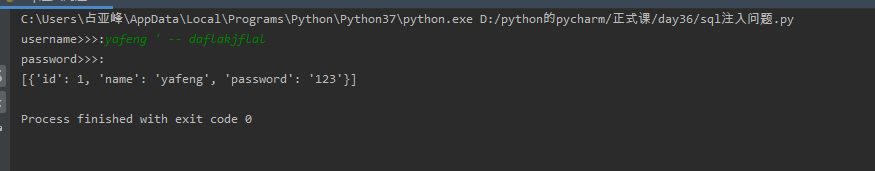
#获取用户输入的用户名密码,然后去数据库中校验
username = input('username>>>:').strip()
password = input('password>>>:').strip()
sql = "select * from emp where name = '%s' and password = '%s'" %(username, password)
cursor.execute(sql)
res = cursor.fetchall()
if res:
print(res)
else:
print('username or password error!')
# 一、只知道用户名
# username>>>:yafeng ' -- daflakjflal
# password>>>:
# [{'id': 1, 'name': 'yafeng', 'password': '123'}]
# 二、用户名密码都不知道
# username>>>:xxx' or 1=1 -- dalfjakdaj
# password>>>:
# [{'id': 1, 'name': 'yafeng', 'password': '123'}]
'''
sql 注入问题
利用特殊符号和注释语法,巧妙的绕过真正的sql校验
解决方案
关键性的数据,不要自己手动去拼接, 而是交由execute帮你去做拼接
'''

- 解决注入问题
import pymysql
coon = pymysql.connect(
user = 'root',
password = '123456',
db = 'day36_1',
host = '127.0.0.1',
port = 3306,
charset = 'utf8'
)
cursor = coon.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
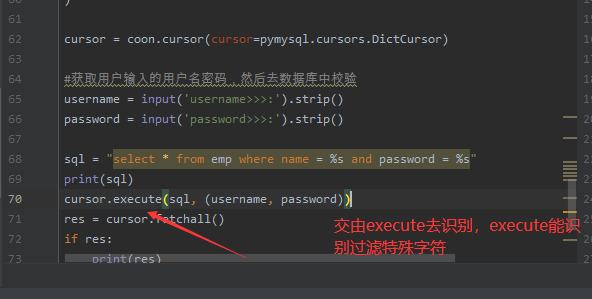
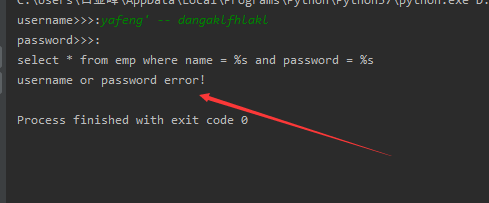
#获取用户输入的用户名密码,然后去数据库中校验
username = input('username>>>:').strip()
password = input('password>>>:').strip()
sql = "select * from emp where name = %s and password = %s"
print(sql)
cursor.execute(sql, (username, password))
res = cursor.fetchall()
if res:
print(res)
else:
print('username or password error!')
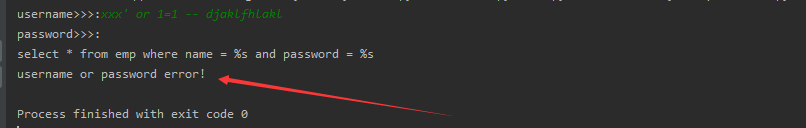
- 数据的增删改查
import pymysql
coon = pymysql.connect(
user = 'root',
password = '123456',
db = 'day36_1',
host = '127.0.0.1',
port = 3306,
charset = 'utf8',
autocommit = True # 自动提交确认
)
cursor = coon.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
#
# # 获取用户输入的用户名和密码, 然后去数据库中校验
# username = input('username>>>:').strip()
# password = input('password>>>:').strip()
#
# sql = "select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s"
# print(sql)
'''
针对增删改的操作 执行重要程度偏高
如果真想要操作 必须有进一步确认操作(commit)
'''
# 增
# sql = "insert into emp(name,password) values('jason',456)"
# 改
# sql = "update emp set name='jason_nb' where id = 2"
# 删
sql = "delete from emp where id = 1"
res = cursor.execute(sql)
print(res)
最新文章
- HBASE数据模型&扩展和负载均衡理论
- python中元组(tuple)的用法
- ace布置小作业: 制作一个简单的电话号码归属地查询软件:JSON解析和Volly发送get请求
- Wisdombud.CommonTool及其应用
- 时间类型(DataTime)赋空值
- jquery如何自定义插件(扩展实例/静态方法)
- GIS应用及OpenGIS介绍
- mysql的优化措施,从sql优化做起
- PHP学习(变量)
- 项目管理实践【四】Bug跟踪管理【Bug Trace and Management】
- aapt: error while loading shared libraries: libstdc++.so.6: wrong ELF class: ELFCLASS64
- opencart配置
- EBS密码加密研究
- 如何修改SpriteBuilder中的按钮禁用启用状态
- 从壹开始 [Admin] 之四 || NetCore + SignalR 实现日志消息推送
- 工作笔记6-java相关
- spring Resource(转)
- Recurrent Neural Network[survey]
- es6 javascript对象方法Object.assign() 对象的合并复制等
- postgresql-磁盘空间不足问题排查