单因素特征选择--Univariate Feature Selection
An example showing univariate feature selection.
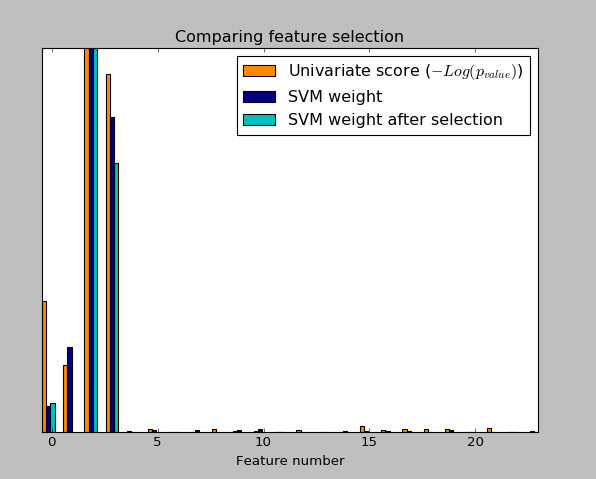
Noisy (non informative) features are added to the iris data and univariate feature selection(单因素特征选择) is applied. For each feature, we plot the p-values for the univariate feature selection and the corresponding weights of an SVM. We can see that univariate feature selection selects the informative features and that these have larger SVM weights.
In the total set of features, only the 4 first ones are significant. We can see that they have the highest score with univariate feature selection. The SVM assigns a large weight to one of these features, but also Selects many of the non-informative features. Applying univariate feature selection before the SVM increases the SVM weight attributed to the significant features, and will thus improve classification.
#encoding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets,svm
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectPercentile,f_classif ###load iris dateset
iris=datasets.load_iris() ###Some Noisy data not correlated
E=np.random.uniform(0,0.1,size=(len(iris.data),20)) ###uniform distribution 150*20
X=np.hstack((iris.data,E))
y=iris.target plt.figure(1)
plt.clf() X_indices=np.arange(X.shape[-1]) ###X.shape=(150,24) X.shape([-1])=24 selector=SelectPercentile(f_classif,percentile=10)
selector.fit(X,y)
scores=-np.log10(selector.pvalues_)
scores/=scores.max() plt.bar(X_indices-0.45,scores,width=0.2,label=r"Univariate score ($-Log(p_{value})$)",color='darkorange')
# plt.show() ####Compare to weight of an svm
clf=svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(X,y) svm_weights=(clf.coef_**2).sum(axis=0)
svm_weights/=svm_weights.max()
plt.bar(X_indices - .25, svm_weights, width=.2, label='SVM weight',
color='navy')
clf_selected=svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
# clf_selected.fit(selector.transform((X,y)))
clf_selected.fit(selector.transform(X),y) svm_weights_selected=(clf_selected.coef_**2).sum(axis=0)
svm_weights_selected/=svm_weights_selected.max() plt.bar(X_indices[selector.get_support()]-.05,svm_weights_selected,width=.2,label='SVM weight after selection',color='c') plt.title("Comparing feature selection")
plt.xlabel('Feature number')
plt.yticks(())
plt.axis('tight')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()
实验结果:
最新文章
- Linux 安装Mono环境 运行ASP.NET(二)
- tcpip
- Openstack命令行删除虚拟机硬件模板flavor
- RestFul API初识
- 《Java程序设计》第一周学习总结
- sql server中分布式查询随笔
- 鼠标划过图片title 提示实现
- express4.x中的链式路由句柄
- Android数字签名解析(二)
- 算法模板——LCA(最近公共祖先)
- AJAX获取JSON WEB窗体代码
- C++文档补充
- JDK1.7+Tomcat6.0+MyEclipse8.6在win7下的安装与配置
- PLSQL分级取数据
- Unity3D Android动态反射加载程序集
- python之路----线程
- Android 处理含有EditText的Activity虚拟键盘
- C# 一些常用的字符串扩展方法
- datatables传参
- stm32 nucleo系列开发板的接口